Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- Higher
Types of data
I can identify the different types of data.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Primary data is collected first-hand, secondary data was collected by someone else.
- Qualitative data is non-numeric information, quantitative is numeric information.
- Quantitative data can be either discrete or continuous.
Keywords
Primary/Secondary data - Primary data refers to data that are directly collected for specific use in an investigation. Secondary data refers to data that were previously collected for a different or unknown purpose.
Qualitative - Qualitative data are data that are non-numerical, and usually describe a quality of something.
Quantitative - Quantitative data are numerical data that can be counted or measured.
Discrete - Discrete data can only take specific numerical values.
Continuous - Continuous data can take any value on a scale to as much precision as we can measure it.
Common misconception
Pupils may think that primary data means data they collect first hand (and no one else can collect it).
Primary data refers to data that are directly collected for specific use in an investigation. This means that a team of researchers could collect the data for you for your investigation and this is still primary data.
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: Types of data, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: Types of data, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Sampling unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each stage of the Statistical Enquiry Cycle to the order it should come in.
Planning
Collecting
Processing and presenting
Interpreting
Communicating and evaluating
Q2.Laura has drawn a scatter graph to display her findings. Which stage of the Statistical Enquiry Cycle does this event fit in?
Q3.Match each stage of the Statistical Enquiry Cycle to an event.
Deciding to research the safety of a new medicine
Testing a new medicine
Using a spreadsheet to analyse the data
Looking at results and deciding what they show
Concluding a new medicine is safe
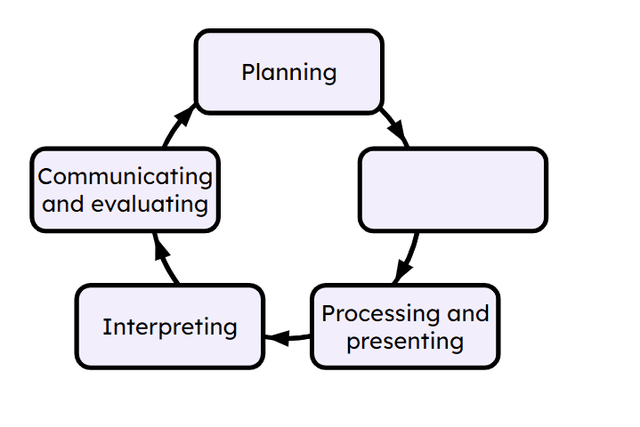
Q4.Which stage is missing from this Statistical Enquiry Cycle?
Q5.Aisha wants to know what type of music students like for the school prom. She plans to ask 'What type of music do you listen to?'. What statistics can she find with the data from this question?
Q6.Sam wants to find out whether pupils who got a high mark in French also did well in English. She collects data for 20 pupils on their end of year exam marks. Sam should draw a graph of the data.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Select all the examples of qualitative data.
Q2.Sofia has some qualitative data. Which summary statistic can she use with her data?
Q3.Andeep collects some data on the cost of meals in the school canteen. Which of these statements are correct?
Q4.Match each type of data to an example.
model of car
number of cars in car park
volume of petrol in car


