Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 10•
- Higher
The effect of enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape
I can understand the effect of an enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape.


- Year 10•
- Higher
The effect of enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape
I can understand the effect of an enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- An enlargement means the object and image are similar.
- All lengths in the object have been multiplied by the scale factor.
- Using index laws, this means the volume has been multiplied by the scale factor cubed.
Keywords
Similar - Two shapes are similar if the only difference between them is their size. Their side lengths are in the same proportions.
Invariant - A property of a shape is invariant if that property has not changed after the shape is transformed.
Enlargement - Enlargement is a transformation that causes a change of size.
Scale factor - A scale factor is the multiplier between similar shapes that describes how large one shape is compared to the other.
Volume - Volume is the amount of space occupied by a closed 3D shape.
Common misconception
I will get different linear scale factors if a measure corresponding lengths in cm vs inches.
Scale factors do not have dimensions, and aren't linked to specific units. If one length is 23 cm (9 inches), and a corresponding length is 69 cm (27 inches), then the scale factor between them is 3, regardless of whether we measured in cm or inches.
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: The effect of enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: The effect of enlargement on the volume of a 3D shape, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Similarity unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The transformation that causes a change in of the object is enlargement.
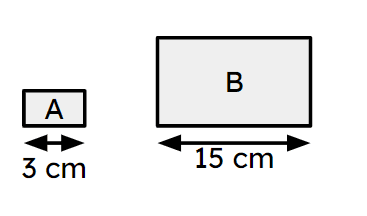
Q2.Rectangles A and B are similar. What is the area scale factor from A to B?
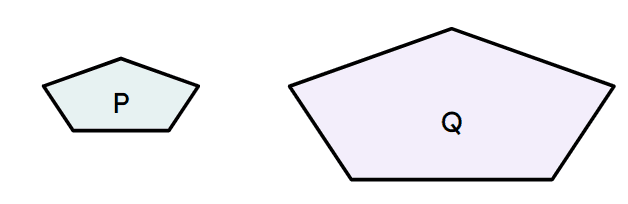
Q3.Shapes P and Q are similar. The perimeter of shape P is 18 cm and the perimeter of shape Q is 72 cm. The area scale factor from P to Q is .
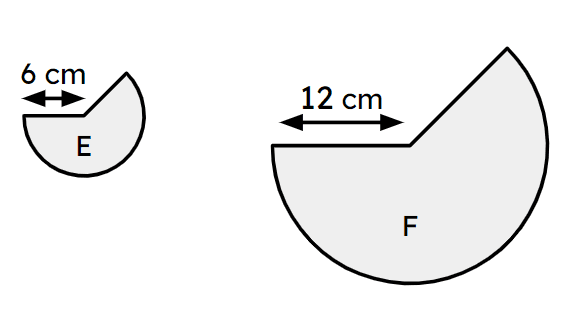
Q4.Sectors E and F are similar. The area of sector E is 30π cm². What is the area of sector F?
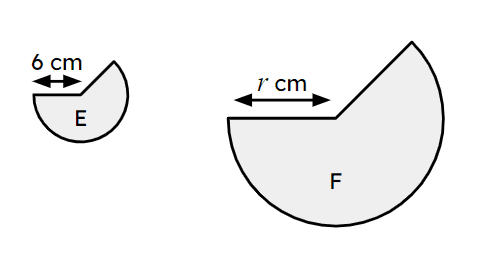
Q5.Sectors E and F are similar. The area of shape E is 24π cm² and the area of sector F is 150π cm². The radius of sector F is cm.
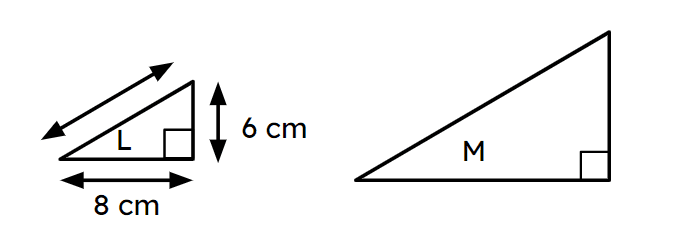
Q6.Triangles L and M are similar. The area of triangle M is 54 cm². What is the perimeter of triangle M?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.__________ is the amount of space occupied by a closed 3D shape.
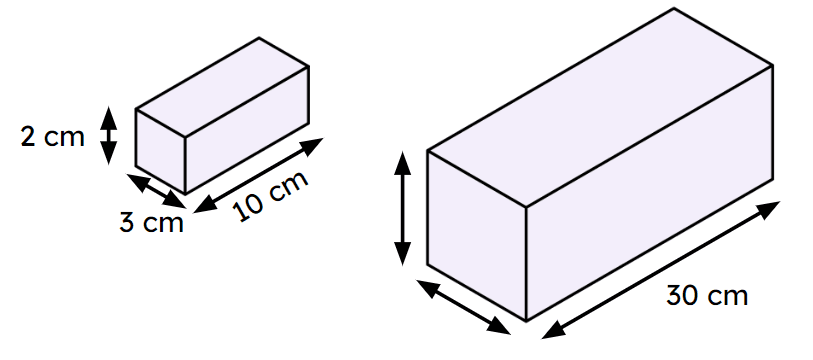
Q2.A cuboid of dimensions 2 cm by 3 cm by 10 cm is enlarged by a scale factor of 3. Work out the volume of the enlarged cuboid.
Q3.Shape A is a 3D shape. Shape A is enlarged by scale factor 3 to give shape B. What is the volume scale factor from A to B?
Q4.Match each linear scale factor to correct the volume scale factor.
Linear scale factor: $$2$$ -
Volume scale factor: $$8$$
Linear scale factor: $$4$$ -
Volume scale factor: $$64$$
Linear scale factor: $$5$$ -
Volume scale factor: $$125$$
Linear scale factor: $$10$$ -
Linear scale factor: $$1000$$
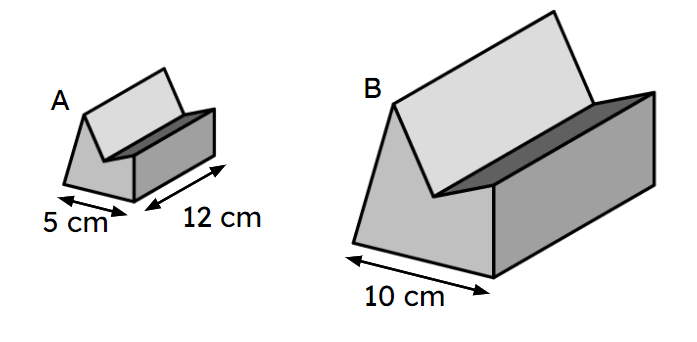
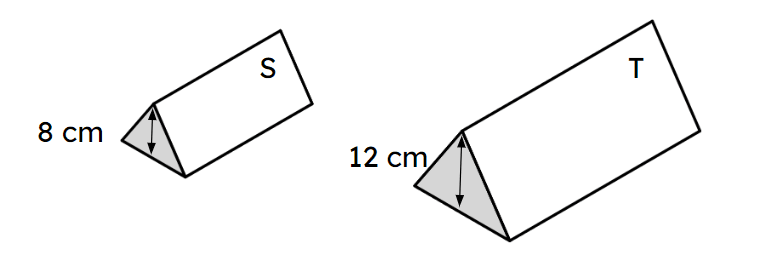
Q5.Prism S and prism T are similar. What is the scale factor of enlargement from prism S to prism T?
Q6.Prism A and prism B are similar. The end face of prism A has an area of 15 cm². The volume of prism B is cm³.