Blood vessels, blood cells and the vascular shunt
I can explain the structure and function of different types of blood vessels and blood cells in the circulatory system.
Blood vessels, blood cells and the vascular shunt
I can explain the structure and function of different types of blood vessels and blood cells in the circulatory system.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart at high pressure. They have thick walls and a smaller lumen.
- Veins carry blood back to the heart. They have thinner walls and contain valves to prevent backflow.
- Capillaries facilitate the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products between blood and tissues.
- Red blood cells transport oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients.
- White blood cells fight infections, platelets enable blood clotting and plasma makes up the main blood volume.
Keywords
Arteries - blood vessel with small lumen and thick muscular walls, carries blood away from the heart
Veins - blood vessel with wide lumen, containing pocket valve, carries blood back towards the heart
Capillaries - thin (one cell thick) blood vessel that allow exchange of materials between the blood and the tissues of the body
Vasoconstriction - when arterioles feeding the areas not needing so much blood constrict (become smaller in diameter) to restrict blood flow to that area
Vasodilation - when arterioles feeding the areas needing more blood dilate (become wider in diameter) to increase blood flow to that area
Common misconception
Arteries always carry oxygenated blood.
The pulmonary artery is the only artery in the body that carries deoxygenated blood as it is pumped back to the lungs to be re-oxygenated. Consequently, the pulmonary vein is the only vein in the body that carries oxygenated blood.
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Blood vessels, blood cells and the vascular shunt, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Blood vessels, blood cells and the vascular shunt, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physical education lessons from the Anatomy and physiology: the cardio-respiratory system unit, dive into the full secondary physical education curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
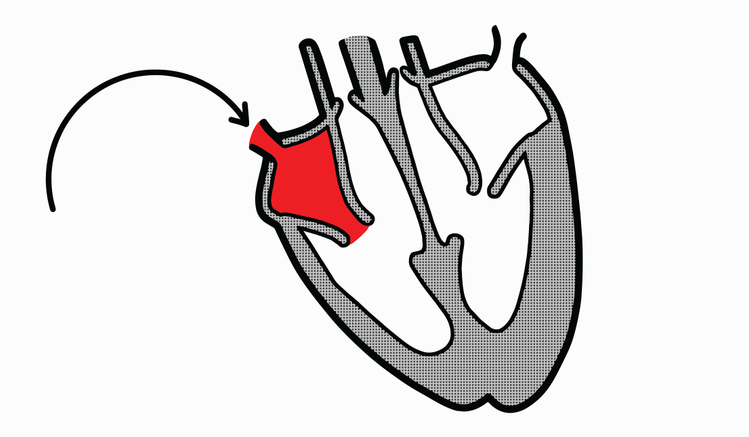
carries oxygenated blood back from the lungs
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
pumps blood out into the aorta
receives deoxygenated blood from the body
pumps blood to the lungs to pick up fresh oxygen supplies
Exit quiz
6 Questions
carry oxygen
fight infection
clot the blood
makes up the majority of the blood volume to help it flow
carry blood away from the heart at high pressure
enable gaseous exchange due to being one cell thick
happens during exercise to remove excess heat
happens during exercise to provide oxygen
happens during exercise to reduce blood flow
happens when cold to reduce heat loss


