Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
Bones and structure of the skeleton
I can locate the major bones in the human body and identify the functions of the skeletal system.
- Year 10
- AQA
Bones and structure of the skeleton
I can locate the major bones in the human body and identify the functions of the skeletal system.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Anatomy and physiology is the study of the structure of the body and how it functions.
- The axial skeleton is a structural framework that contains the cranium, vertebrae, ribs and sternum.
- The appendicular skeleton contains the bones of the upper and lower limbs, the scapula, clavicle and pelvis.
- Muscles attach to bones and work together to create movement.
- Bones protect vital organs, produce red blood cells and store minerals.
Keywords
Anatomy - the branch of science concerned with the physical structures of the body
Physiology - the study of how the human body works or functions
Musculoskeletal - a combination of the muscular and skeletal system comprising of muscles, bones, joints and connective tissues
Skeleton - the structural frame that supports the body and is made up by a collection of bones
Joint - a place where two or more bones meet (articulate)
Common misconception
Mixing up the different body systems and terminology used for each (for example, not realising the cardiorespiratory system refers to the heart and lungs).
Ensure pupils understand that muscular means muscles, skeletal means bones, cardio means heart, vascular means blood vessels and respiratory means lungs.
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Bones and structure of the skeleton, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Bones and structure of the skeleton, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physical education lessons from the Anatomy and physiology: the musculoskeletal system unit, dive into the full secondary physical education curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following is an example of a bone?
Q2.The cranium is another name for the ...
Q3.The column is a collection of bones that protects the spinal cord.
Q4.The help with breathing and also protect the heart and lungs.
Q5.The place that two or more bones meet to enable movement is called a ...
Q6.Match the following bodily systems with their function.
allows movement when muscles contract to leverage bones
pumps blood around the body
enables gaseous exchange to get oxygen into the body
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The tibia and fibula are both located in which part of the body?
Q2.Which of the following bones do not articulate at the hip?
Q3.Name the bone identified in the image below.
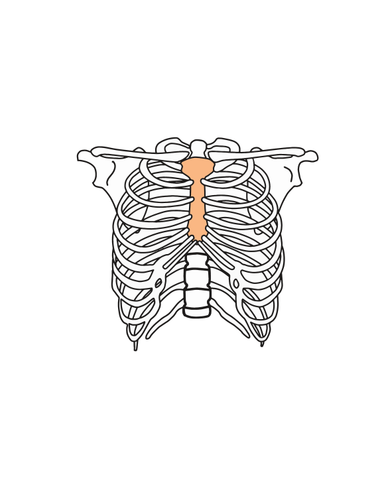
Q4.Match the main function to the following bones.
muscle attachment enabling movement
protection of the brain
provide a framework to hold the body upright and protect spinal cord


