Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- Edexcel
Types of muscle and muscle fibre
I can identify different types of muscle and different types of muscle fibre and explain their function
- Year 10
- Edexcel
Types of muscle and muscle fibre
I can identify different types of muscle and different types of muscle fibre and explain their function
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- All skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, they are under our conscious control (e.g. biceps).
- Involuntary muscles work without our conscious control and include the walls of our digestive system and blood vessels.
- Cardiac muscle is a specialist type of involuntary muscle that makes up the thickest layer of the heart.
- Fast twitch muscle fibres with a high speed and force of contraction are used for short, intense exercises.
- Slow twitch muscle fibres that are resistant to fatigue are used for long distance events.
Keywords
Voluntary - when something is under our conscious control
Involuntary - when something is not under our conscious control
Cardiac muscle - involuntary muscle found in the heart
Slow twitch - a type I muscle fibre type with slow speed and low force of contraction
Fast twitch - a type II muscle fibre with a fast speed and high force of contraction
Common misconception
Pupils may get confused with the different names of fast/ slow and type I/ type II muscle fibres.
The word slow has an O in it and these fibres use oxygen to contract slowly and aerobically. They are our body's first choice of muscle fibre due to fatigue resistance, hence type I.
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Types of muscle and muscle fibre, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Types of muscle and muscle fibre, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physical education lessons from the Anatomy and physiology: the musculoskeletal system unit, dive into the full secondary physical education curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which joint allows abduction and adduction?
Q2.Other than moving our limbs, what else do our muscles support?
Q3.Identify the movement occurring at the hinge joint.
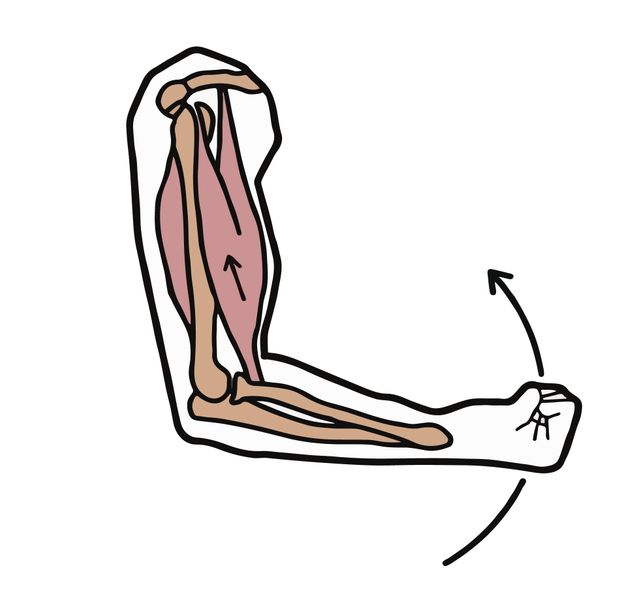
Q4.Match the muscle type to the correct description.
when something is under our conscious control
when something is not under our conscious control
involuntary muscle found in the heart
Q5.Where is the cardiac muscle found?
Q6.Match the type of muscle fibres to the activity described.
work at low intensity over a long period of time
work at quick, high intensity for short periods of time
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Voluntary and involuntary muscles are found in the body. What is the other type of muscle found in the body?
Q2.Which of the following are examples of voluntary muscles?
Q3.Match the keywords to their correct defintion.
when something is under our conscious control
when something is not under our conscious control
involuntary muscle found in the heart
a type I muscle fibre with slow speed and low force of contraction
a type II muscle fibre with a fast speed and high force contraction
Q4.Fast twitch muscle fibres work explosively for a period of time.
Q5.Which muscle fibres have an excellent supply of oxygen via the capillaries?
Q6.Match the athlete to the muscle fibre that would be most useful to their performance.
type I
type IIa
type IIx


