Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Resistance of a hot metal
I can explain why the resistance of a metal filament changes as the p.d. across it increases.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Resistance of a hot metal
I can explain why the resistance of a metal filament changes as the p.d. across it increases.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- As the p.d. across a filament lamp increases, it gets hotter and current through it increases in a non-ohmic way.
- The greater the p.d. across a filament lamp, the greater its resistance.
- A metal is made of a lattice of positively charged ions with negatively charged electrons between.
- As a current flows through metal, electrons moving through the ion lattice cause it to vibrate more vigorously.
- The more vigorously the ions (ion lattice) vibrate, the hotter the metal and the higher its resistance.
Keywords
Filament lamp - a type of lamp that uses a hot wire to emit light
Ohmic conductor - a conductor for which the current is directly proportional to the p.d.
Directly proportional - a relationship between variables in which one is a multiple of the other
Metal ion - a metal atom that has lost one or more outer electrons and has become positively charged
Free electron - an electron from the outer shell of an atom that is free to move from ion to ion through a metal
Common misconception
The gradient of an I-V graph is equal to 1/R because I = V ÷ R.
Explain how the equation for a straight line graph y = mx + c does not apply in this case because the graph is not a straight line.
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Resistance of a hot metal, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Resistance of a hot metal, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Circuit components unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following components is represented by the circuit symbol shown?
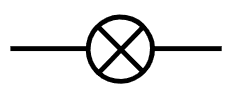
Q2.What happens to the current through a filament lamp as the p.d. across it is increased?
Q3.What is the resistance of a filament lamp if it has a current of 0.25 A when a p.d. of 0.5 V is applied across it?
Q4.Which of the following statements about the I–V graph of a filament lamp is correct?
Q5.If the p.d. across a filament lamp increases at a steady rate, how does the current through it change as the p.d. becomes higher?
Q6.What is the resistance of the filament lamp at a p.d. of 3.0 V, according to the I–V graph shown?
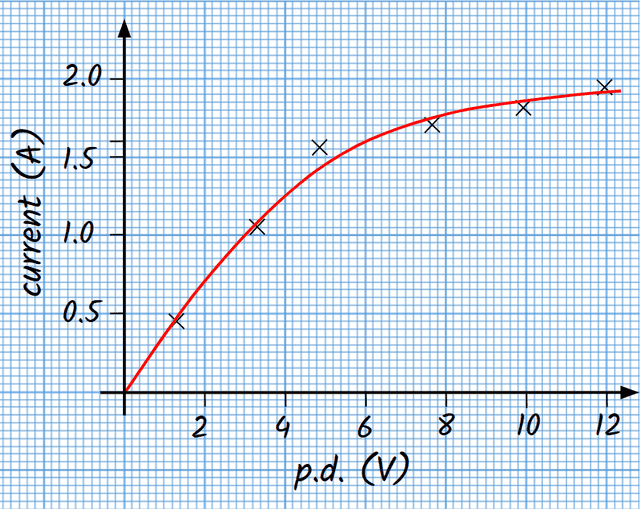
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following components does the I–V graph shown represent?
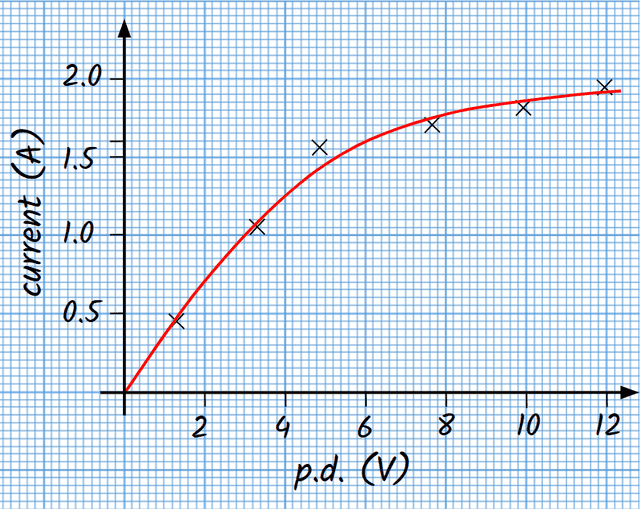
Q2.Which of the following is an ohmic conductor?
Q3.Which of the following statements about ohmic conductors and non–ohmic conductors is correct?
Q4.In the model of a metal shown, what do the blue circles represent?
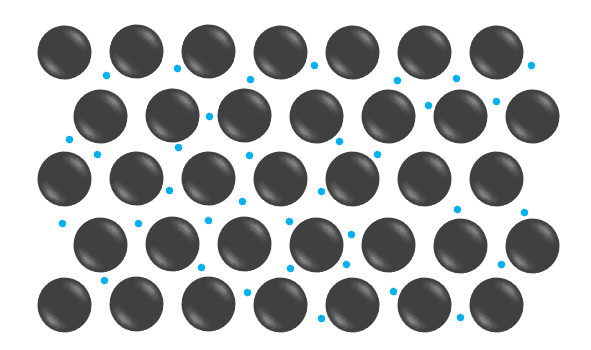
Q5.In the model of a metal shown, what do the black circles represent?



