Adding components to a parallel circuit
I can use the rules for current and potential difference in a parallel circuit and explain the effects of adding a component.
Adding components to a parallel circuit
I can use the rules for current and potential difference in a parallel circuit and explain the effects of adding a component.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
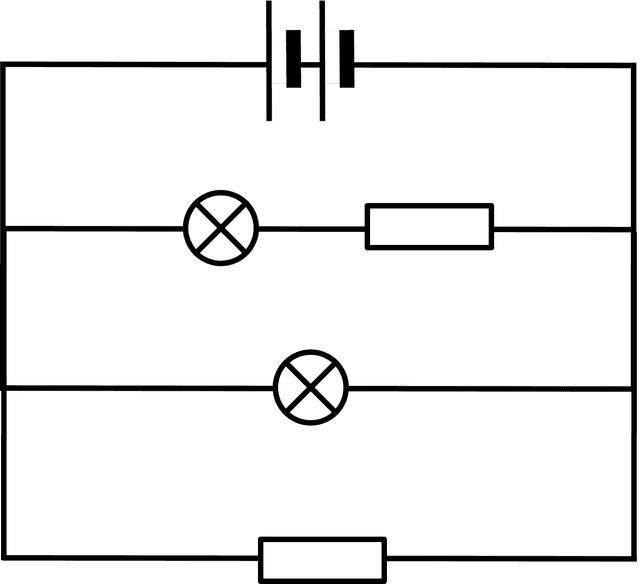
- The p.d. across each branch of a parallel circuit is the same as the p.d. across the battery.
- The current through each branch of a parallel circuit adds up to the current through the battery.
- Adding a component in a new branch of a parallel circuit reduces the resistance of the circuit.
- Adding a component to an existing branch of a parallel circuit increases the resistance of the circuit.
- The p.d. across the terminals of a battery does not change when components are added to a circuit.
Keywords
Electric charge - an electrical property; it can either be positive or negative
Parallel circuit - a circuit with separate branches connected to the battery
Electric field - the invisible field around a charged object that causes other charges to experience a force
Potential difference (p.d.) - the voltage or a measure of the ‘push’ on electrons in a circuit
Electric current - a measure of the amount of charge passing a given point in one second
Common misconception
To solve circuits you need only to put numbers into equations.
Talk through circuits with pupils before analysing them in order to develop an intrinsic understanding of how circuits work; research shows this improves pupils’ problem solving ability for electric circuits.
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Adding components to a parallel circuit, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Adding components to a parallel circuit, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electric fields and circuit calculations unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
1.5 V cells, identical bulbs in holders, ammeters and electrical leads
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions