Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- OCR
- Foundation
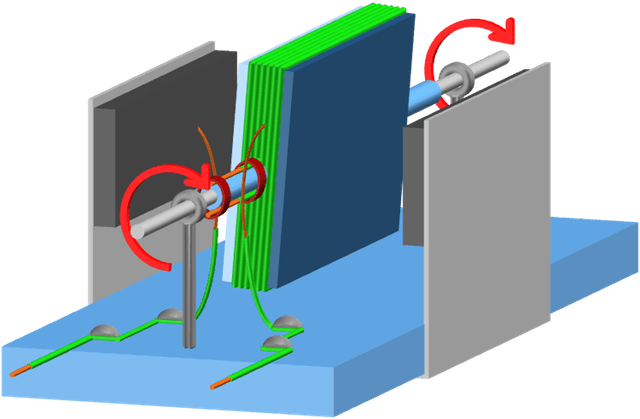
An electric motor
I can explain how connections in a motor enable its coil to be driven continually in one direction.
- Year 11
- OCR
- Foundation
An electric motor
I can explain how connections in a motor enable its coil to be driven continually in one direction.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Wire in a motor is insulated so that the current flows around the coil
- Connections in a motor slide over each other to prevent tangled wires
- When the coil in a motor kit is horizontal it is connected and a force acts on the sides 90 deg. to the magnetic field
- Every half–turn, the coil connections in a motor kit swap over and change the direction of current through the coil
- Each side of a coil in a motor kit at 90º to the magnetic field is pushed alternatively up then down every half turn
Keywords
Electrical insulator - is a material that does not conduct electric current
Motor coil - a coil of insulated wire that spins inside an electric motor when a current flows through it
Axle - a rod at the centre of wheels and gears around which they turn
Yoke - in a motor kit, a U–shaped piece of iron that holds two magnets in place to create a uniform magnetic field
Common misconception
Pupils find it challenging to think about how current flows through the connections and around the coil in the motor.
Take pupils step–by–step through the building of a motor from a motor kit and provide an opportunity for pupils to build their own working motor to help them to consolidate their understanding.
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: An electric motor, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: An electric motor, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetism unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Commercially available motor kits that can be used to construct electric motors, together with a 3 V power pack, connection leads and crocodile clips.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A material that allows an electric current to flow is called an electrical conductor. A material that does not allow an electric current to flow is called an electrical .
Q2.The diagram shows a magnetic field between two magnets. The north–seeking and south–seeking poles are shown but the arrows are missing from the field lines. Which way should the arrows point?
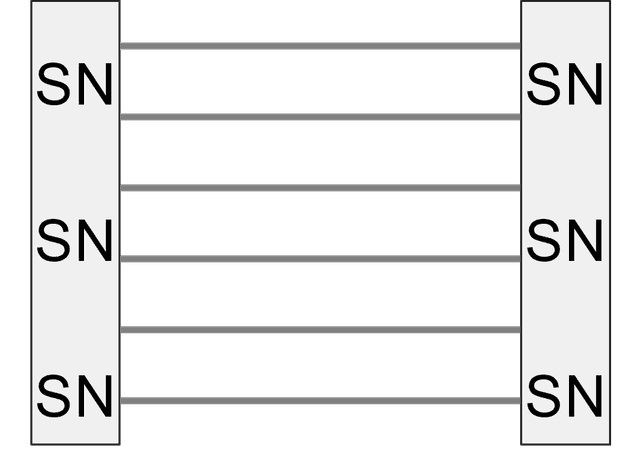
Q3.A magnetic field with equally spaced field lines is described as .
Q4.Which of the following statements describes the motor effect?
Q5.When using Fleming’s rule to predict the direction of the force, current or magnetic field in the motor effect, which of the following are correct?
Q6.The diagram shows a current–carrying wire in a uniform magnetic field. Black arrows show magnetic field direction and a grey arrow shows current direction. In which direction is the force on the wire?
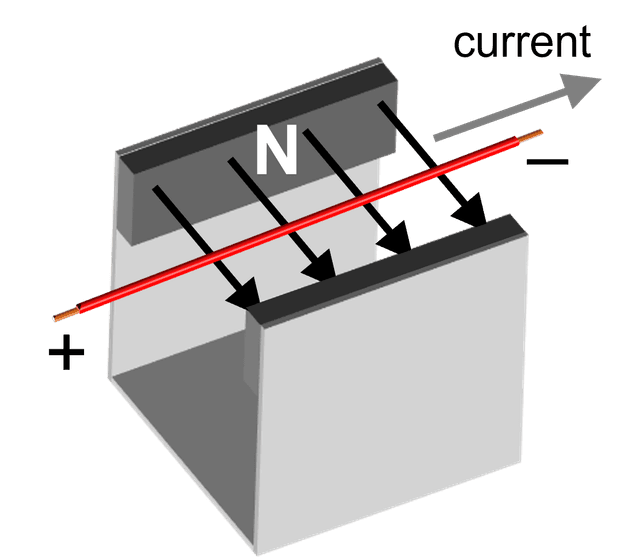
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each part of a motor with its description.
a rod about which the coil turns
insulated wire wound into many turns; rotates when the motor runs
a U–shaped piece of iron that holds two magnets in place
Q2.The diagram shows a simple electric motor from one end, with some of its parts labelled with the letters A to D. Match each letter with the name of the part.
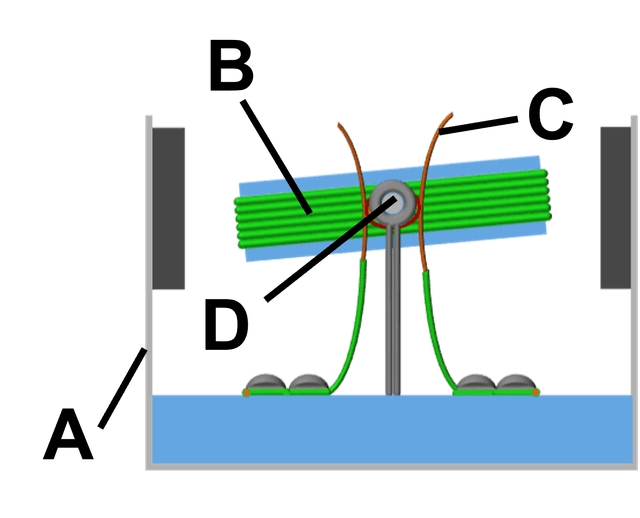
yoke
coil
wire contact
axle
Q3.Which of the following explains why the coil of a motor turns when it is connected to a suitable power supply?
Q4.A pupil tries to make an electric motor. They join the wire contacts onto the ends of the coil. Why does the motor not work correctly when a battery is connected to the other ends of the contacts?
Q5.The diagram shows a motor that is powered by a battery. When the coil is in the vertical position shown, there is no electrical contact between the coil and the battery. What happens next, and why?