The spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
I can explain what is meant by the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
The spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
I can explain what is meant by the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
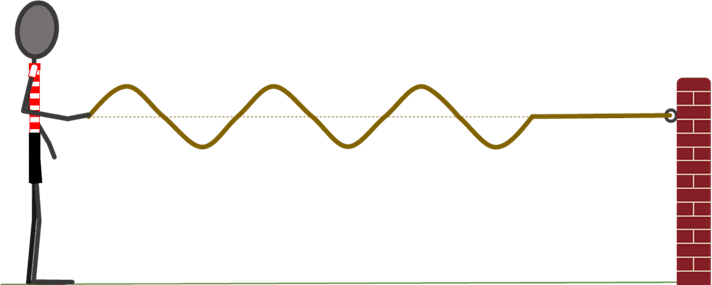
- Electromagnetic waves/radiation are transverse oscillations (ripples) in electric and magnetic fields.
- The visible spectrum shows the range of different frequencies (colours) of visible light waves (visible EM radiation).
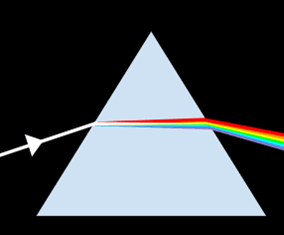
- In the visible spectrum, violet light has the highest frequency and refracts more than red as it slows more in glass.
- The EM spectrum shows the range of frequencies that EM waves can have (radio, microwave, IR, visible, UV, X-ray, gamma).
- EM waves in different frequency ranges have the same speed in air, but interact differently with different materials.
Keywords
Electromagnetic wave - Electromagnetic waves are oscillations/ripples in electric and magnetic fields.
Frequency - The frequency of a wave gives the number of oscillations that occur per second.
Spectrum - A spectrum is a continuous range or scale.
Refraction - Refraction is when waves enter a new material and change direction.
Radiation - Anything that is emitted (given out) from a system and transfers energy away from that system can be called radiation.
Common misconception
The different 'kinds' of EM radiation are different phenomena to each other and to visible light. Pupils may also think all radiation is dangerous, none is natural and that light is not radiation.
Each 'kind' of EM radiation is the same phenomena as light (i.e. waves/ripples in electric and magnetic fields) just with different frequencies and wavelengths. Try to refer to different frequencies/frequency ranges rather than different 'kinds'.
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: The spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: The spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetic waves unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions
Security pen ink can only be seen when this is shone onto it.
Thermal cameras detect this.
This is used to transmit television signals over long distances.
This is used to make images of a patient’s bones in hospital.


