Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Higher
Strength of an electromagnet
I can accurately measure the strength of an electromagnet to analyse how different factors affect it.


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Higher
Strength of an electromagnet
I can accurately measure the strength of an electromagnet to analyse how different factors affect it.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A soft iron core increases the strength of an electromagnet because it becomes magnetised when it is turned on.
- The more tightly wound the coil of wire is in an electromagnet, the stronger its magnetic field.
- The greater the current through the coil of an electromagnet, the stronger its magnetic field.
- The strength of an electromagnet is directly proportional to the current through it.
Keywords
Coil of an electromagnet - An insulated wire wound into the shape of a spring.
Turn of wire - A single loop of wire in a coil.
Soft iron - Very pure iron that cannot be made into a permanent magnet.
Directly proportional to - Describes the relationship between two variables, in which doubling the value of one variable doubles the value of the other.
Error bars - These show the accuracy of each measurement on a graph.
Common misconception
Digital ammeters are always accurate to the smallest amount they display.
Show pupils a copy of the specifications of the ammeters they are using that show how accurate they really are.
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Strength of an electromagnet, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Strength of an electromagnet, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetism unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
For each group, or for a demonstration: a digital balance, boiling tube, clamp and stand, lab pack, ammeter, connecting wires, single core insulated wire, two crocodile clips and a bar magnet.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following types of magnet is the magnetic field of an electromagnet most similar to?
Q2.A pupil wants to make a strong electromagnet that loses its magnetism completely when switched off. Which of these is a suitable core material? (Note: soft/hard here means magnetically soft/hard.)
Q3.Which of the following have a magnetic field around them?
Q4.How many newtons are equal to a force of 1 mN?
Q5.Which of the following statements is correct? (Note: assume the objects are on Earth.)
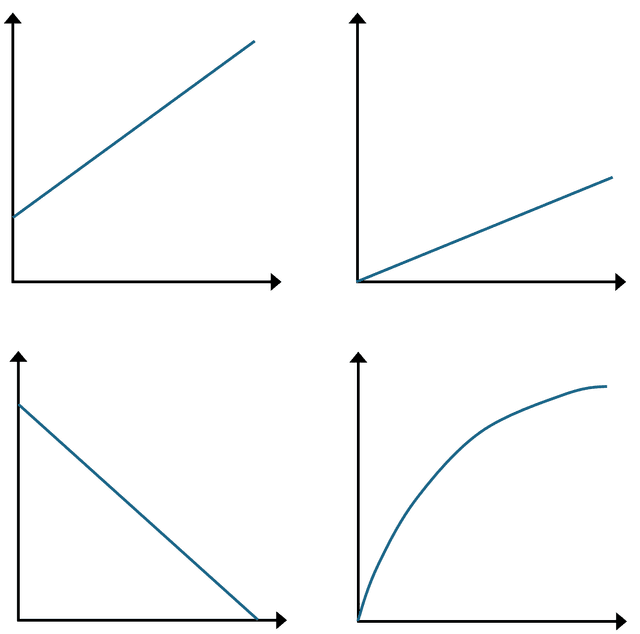
Q6.Two variables, $$a$$ and $$b$$, are directly proportional. Which of the following statements are correct?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.When field lines are drawn to represent a magnetic field, which of the following represents a region in which the field is stronger?
Q2.Which of the following increase the strength of the magnetic field around a coil of wire with a fixed diameter?
Q3.If all other variables are kept constant, the strength of an electromagnet is always …
Q4.An electromagnet’s strength can be investigated using the apparatus shown. When the electromagnet is switched on, there is a positive mass reading on the balance. Which of the following are correct?
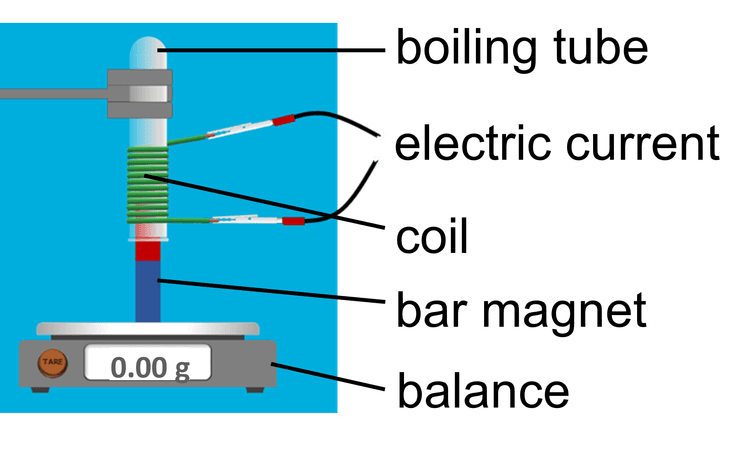
Q5.On a graph of experimental results, lines can be drawn through each point to show the accuracy of the two measurements used to plot it. What is the name of these lines?
Q6.How many of these graphs show a directly proportional relationship?