Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Higher
The motor effect
I can describe the force acting on a current–carrying wire or loop in a uniform magnetic field.


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Higher
The motor effect
I can describe the force acting on a current–carrying wire or loop in a uniform magnetic field.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The magnetic field lines around a current-carrying wire are concentric circles
- In a uniform magnetic field, a current carrying wire is forced in one direction
- Fleming’s left–hand rule can be used to predict the direction of movement of a current–carrying wire in a magnetic field
- The force on a current–carrying conductor at right angles to a magnetic field, F, is found using F = B I l.
- Opposite sides of a conducting coil in a uniform magnetic field are forced to move in opposite directions
Keywords
Uniform magnetic field - has evenly spaced field lines and the strength of the magnetic field is the same everywhere
Fleming’s left-hand rule - indicates the direction a conducting wire is forced to move in a uniform magnetic field
Magnetic flux density, B - is a measure of the strength of a magnetic field
Tesla (T) - is the unit that magnetic flux density is measured in
Common misconception
It is not clear how the magnetic field around a conducting wire interacts with a uniform magnetic field.
Focus on observing and predicting the direction that a conducting wire is forced in by a uniform magnetic field, and openly admit that explaining this in terms of how the magnetic field interact is too challenging to include in the syllabus.
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: The motor effect, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: The motor effect, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetism unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.In a drawing of the magnetic field lines around a magnet, the field lines are closer together in some areas than others. Which of the following statements is correct?
Q2.What do the directions of magnetic field lines represent?
Q3.A compass usually points north. If the needle of a compass is deflected (changes direction) so that it no longer points north, which of the following are possible explanations?
Q4.Which of the following statements are correct?
Q5.Two variables have this relationship: whenever the value of one variable is multiplied by a number, the value of the other variable is multiplied by the same number. The two variables are directly...
Q6.Two equal and opposite forces act on the ends of a ruler as shown by the arrows. The ruler is initially stationary. Which of the following describes what happens to the ruler?

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following statements about magnetic flux density are correct?
Q2.Which of the following describes the magnetic field lines near a straight current-carrying wire?
Q3.Which of the following are characteristics of a uniform magnetic field?
Q4.Fleming’s left-hand rule can be used to predict the direction of the force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field. Match each digit with what it represents in the left-hand rule.
first finger -
represents the magnetic field direction
second finger -
represents the direction of the current in the wire
third finger -
is not used in Fleming’s left-hand rule
thumb -
represents the direction of the force on the wire
Q5.A 12 cm length of straight wire carrying a current of 1.2 A is in a uniform magnetic field with flux density 0.50 T. The size of the force on the wire is N.
Q6.The diagram shows a current-carrying loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field. Three sides of the loop are labelled P, Q and R. Match each side to a description of the force acting on it.
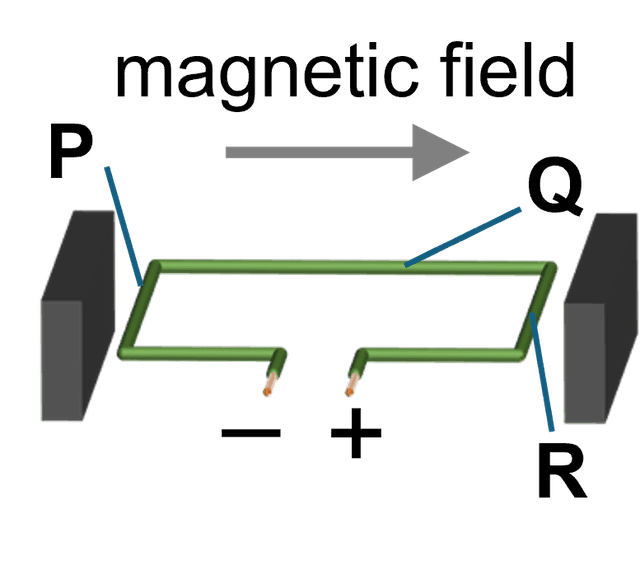
side P -
An upwards force acts.
side Q -
No force acts.
side R -
A downwards force acts.

