Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 10•
- AQA•
- Higher
Measuring acceleration analysis (v = s ÷ t, a = Δv ÷ t)
I can explain how to measure acceleration accurately.


- Year 10•
- AQA•
- Higher
Measuring acceleration analysis (v = s ÷ t, a = Δv ÷ t)
I can explain how to measure acceleration accurately.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A dynamics trolley has a steady acceleration down a steep ramp.
- Acceleration = change of velocity ÷ time and change in velocity = final velocity – initial velocity
- Light gates can improve accuracy of measurement of instantaneous velocity and reduces random errors.
- For a fair test, total mass of the system must be kept constant.
- A compensated ramp can counteract the effect of friction.
Keywords
Compensated ramp - A ramp with a slope to counteract the effect of friction.
Final velocity - The final velocity of an object is the velocity it finishes with after a phase of motion.
Light gate - A light gate can be used to measure velocity. It uses an infrared beam to turn a timer on and off as an object passes through.
Repeatable - Measurements are repeatable if they are very similar when the same procedure is carried out by the same person or team.
Uniform acceleration - When the acceleration is constant, it is described as uniform acceleration.
Common misconception
Pupils may compare the accelerations of objects on the basis of final velocities and may fail to take into account the time interval over which the change in velocity occurred.
Provide pupils with opportunity to analyse measurements of changes in velocity in which the starting velocities vary. A pair of light gates at two positions along the ramp will allow this.
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Measuring acceleration analysis (v = s ÷ t, a = Δv ÷ t), download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physics lesson on: Measuring acceleration analysis (v = s ÷ t, a = Δv ÷ t), download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Measuring and calculating motion unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A student measures the time taken for a toy parachute to fall from a particular height. She repeats the measurement and gets these results: 1.60 s, 1.53 s, 1.52 s. The mean time taken is s.
Q2.A toy car travels at a constant velocity along a straight track. It travels 90 cm in 20 s. The velocity of the toy car is m/s along the track.
Q3.A car accelerates steadily from rest to 20 m/s in a time 8.0 s. The acceleration of the car is m/s$$^2$$.
Q4.A student measures the acceleration of a trolley along a slope for different values of the force pulling the trolley. Which of these is the independent variable in this experiment?
Q5.A trolley travels down a slope. It is stationary at the start and gets faster as it moves. A student takes measurements and calculates: (distance travelled) ÷ (time taken). What has the student found?
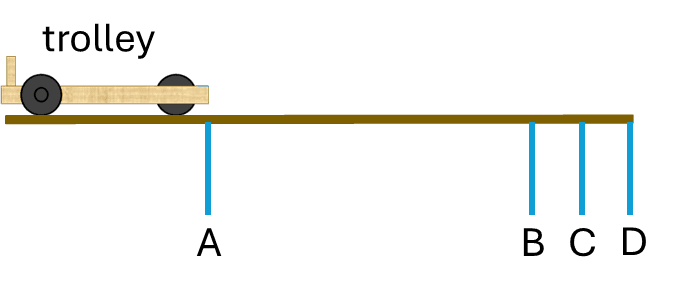
Q6.A trolley is stationary at position A and then accelerates along the track. A student wants to measure the trolley’s average acceleration between A and C. Which of these calculations should be used?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A is an instrument that uses an infrared beam to turn a timer on and off as an object passes through.
Q2.A trolley takes 3.50 s to travel along a ramp. Its starting velocity is 0 and its final velocity is 0.42 m/s. The acceleration of the trolley is m/s$$^2$$.
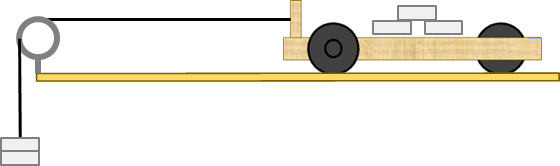
Q3.A student wants to find the relationship between force and acceleration of a trolley. He will use masses on a hanger to pull the trolley. To make the test fair, how should he increase the force?
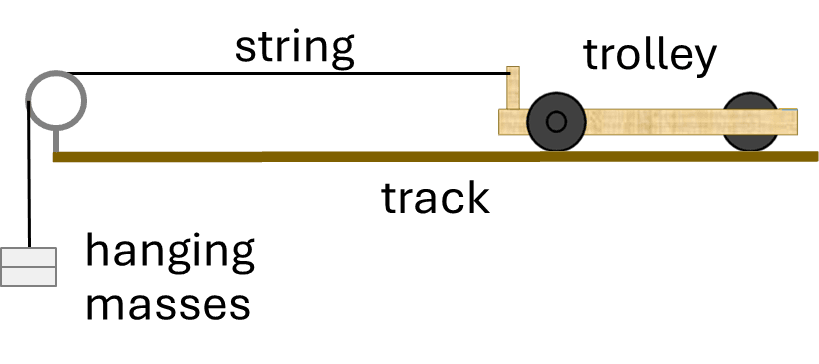
Q4.The picture shows a trolley with three 100 g masses resting on it, and two 100 g masses attached to the trolley by a string. If friction can be ignored, what is the accelerating force on the trolley?