Myths about teaching can hold you back
Learn why
New
New
Lesson 10 of 12
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
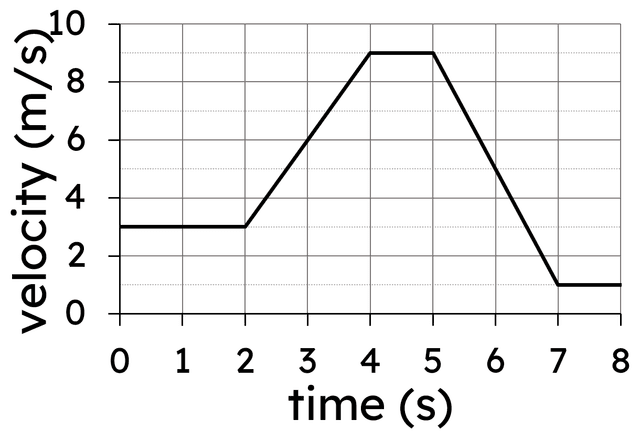
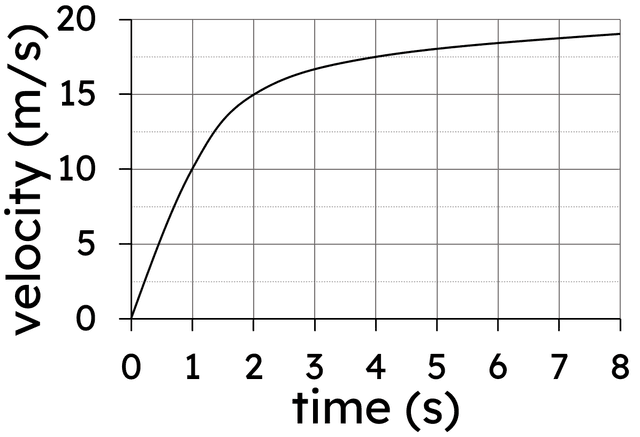
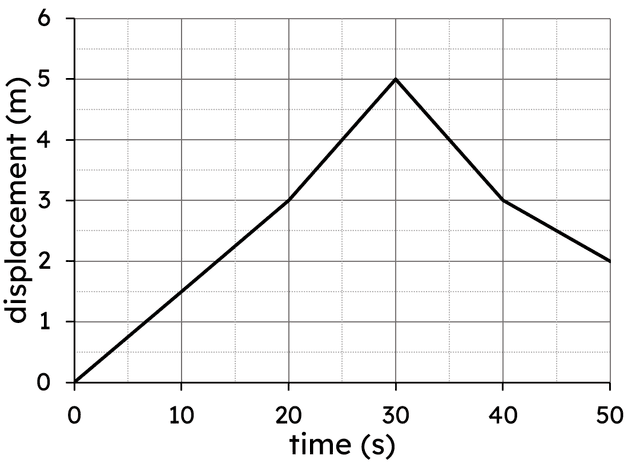
Velocity-time graphs: acceleration and distance travelled (a = Δv/t)
I can read information from velocity-time graphs and calculate acceleration and distance travelled.
Lesson 10 of 12
New
New
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
Velocity-time graphs: acceleration and distance travelled (a = Δv/t)
I can read information from velocity-time graphs and calculate acceleration and distance travelled.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Assessment exit quiz
Download quiz pdf