Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- Edexcel
- Higher
Applications of motor and generator effects
I can explain how a loudspeaker and a microphone work.
- Year 11
- Edexcel
- Higher
Applications of motor and generator effects
I can explain how a loudspeaker and a microphone work.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A sound can be represented by an electronic signal changing in time to match the sound wave.
- Loudspeakers use the motor effect to convert electrical signals into sound waves.
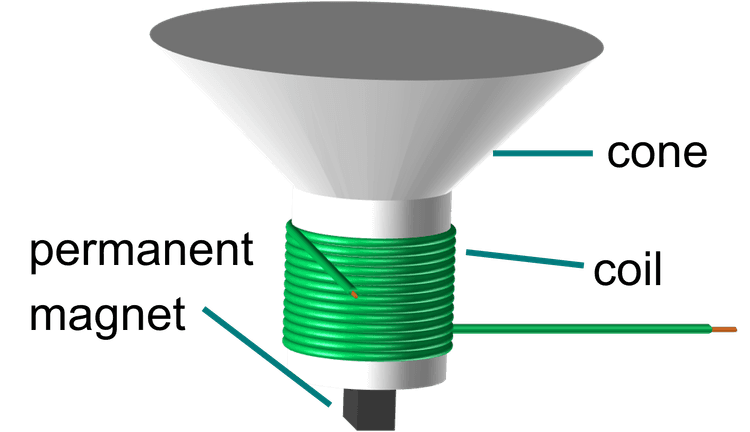
- A moving–coil loudspeaker is made from a cone connected to a coil of wire that moves in relation to a fixed magnet.
- Microphones use the generator effect to convert sound waves into electrical signals.
- A moving–coil microphone is made from a diaphragm connected to a coil of wire that moves in relation to a fixed magnet.
Keywords
Oscilloscope - A piece of equipment that can display a representation of a sound wave.
Motor effect - The effect of causing movement between a magnet and an electromagnet.
Moving-coil loudspeaker - A loudspeaker that produces sound using the motor effect.
Generator effect - The effect of inducing a current by the relative movement of a circuit and a magnetic field.
Moving-coil microphone - A microphone that produces an electric signal from sound using the generator effect.
Common misconception
It is common for pupils to hold the misunderstanding that stationary magnetic fields can attract or repel electric charge or to conflate magnetic and electrostatic effects.
Provide opportunities for pupils to explain applications of the motor effect and the generator effect in order to consolidate a scientific understanding.
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Applications of motor and generator effects, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Applications of motor and generator effects, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetism unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Making a loudspeaker: A4 sheet of thin card, short length of broom handle, single core insulated wire, strong bar magnet, thread, sticky tape, access to a signal generator and leads.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The abbreviation ‘p.d.’ stands for an electrical quantity. What is the full name of this quantity and what is its unit?
Q2.Each of the diagrams shows a wave, with distance along the horizontal axis. All of the diagrams have the same scale. Which two of these waves have the same amplitude?
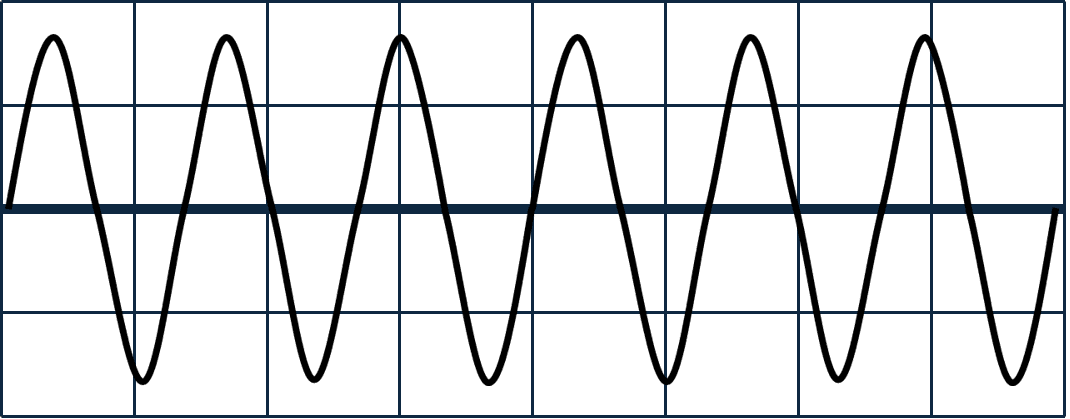
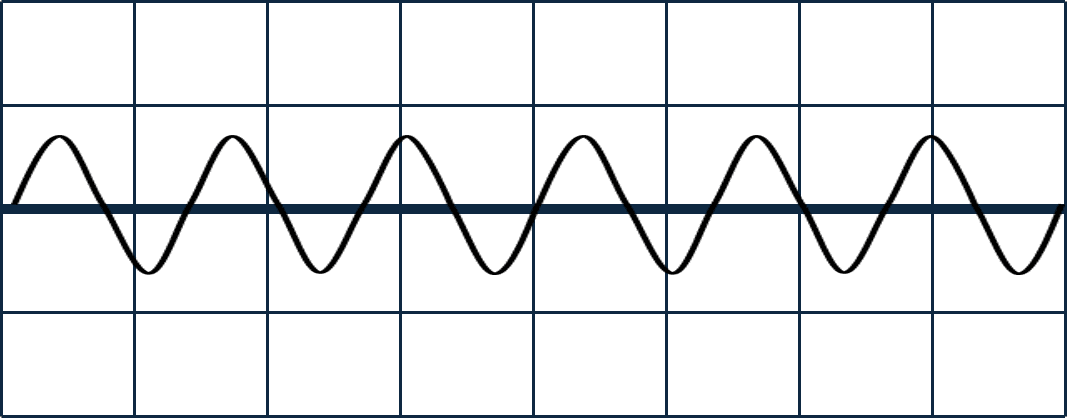
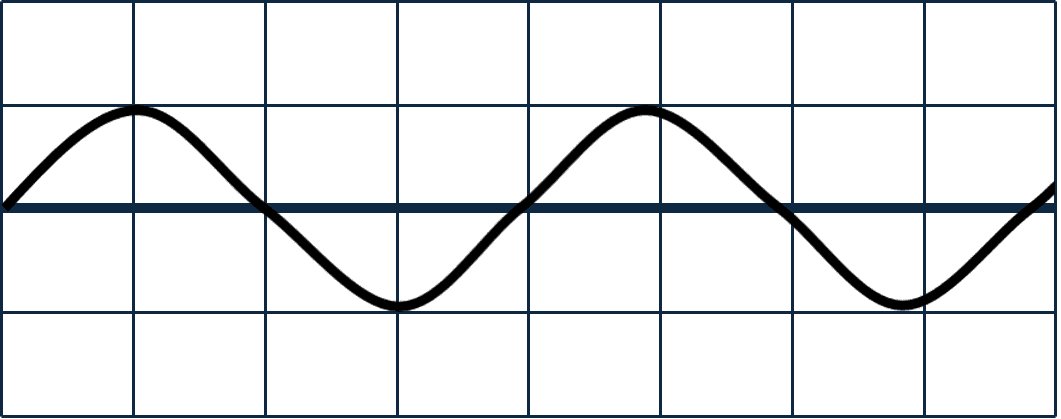
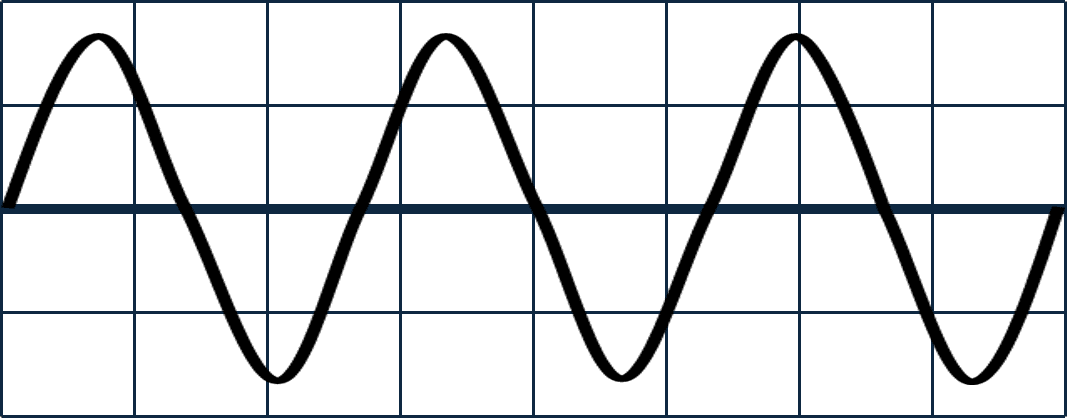
Q3.An object makes a sound. Which of the following must the object be doing?
Q4.Which of the following are correct definitions of the frequency of a wave?
Q5.Which of the following statements are correct?
Q6.When a loudspeaker makes a sound, a part of it called the cone moves backwards and forwards. How does the motion of the cone change if the loudspeaker now makes a louder sound with the same pitch?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each of the following devices to a description of what it does.
displays a representation of a sound wave
produces sound from an electronic signal
produces an electronic signal from sound
Q2.Each of the diagrams shows an oscilloscope trace of a sound wave. All of the diagrams have the same scale. Which of the sound waves have the same pitch?
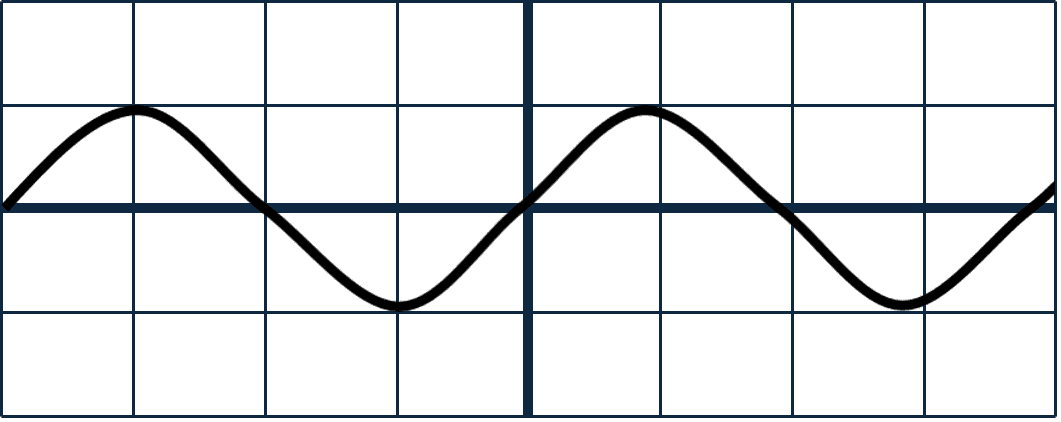
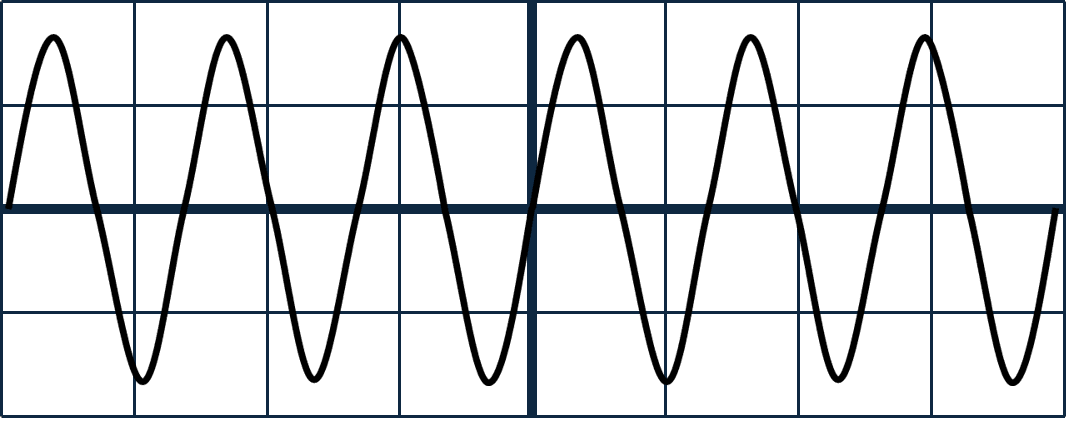
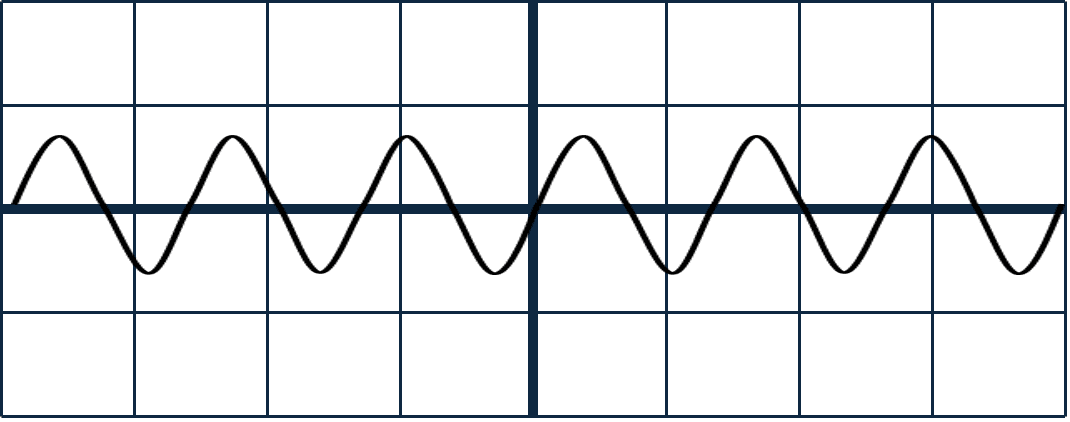
Q3.The diagram shows the coil, cone and permanent magnet of a loudspeaker. The coil is connected to an AC power supply. Which of the following statements are correct?