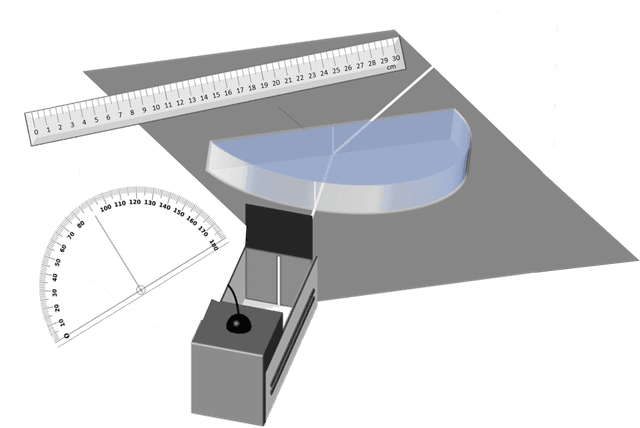
Refraction through a semicircular block
I can describe and explain when refraction happens and when total internal reflection happens at boundaries between media.
Refraction through a semicircular block
I can describe and explain when refraction happens and when total internal reflection happens at boundaries between media.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
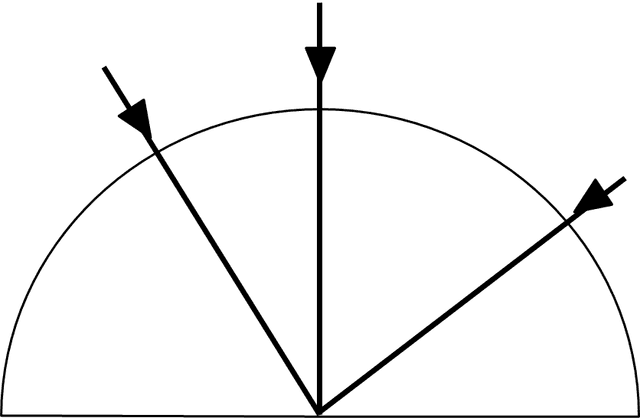
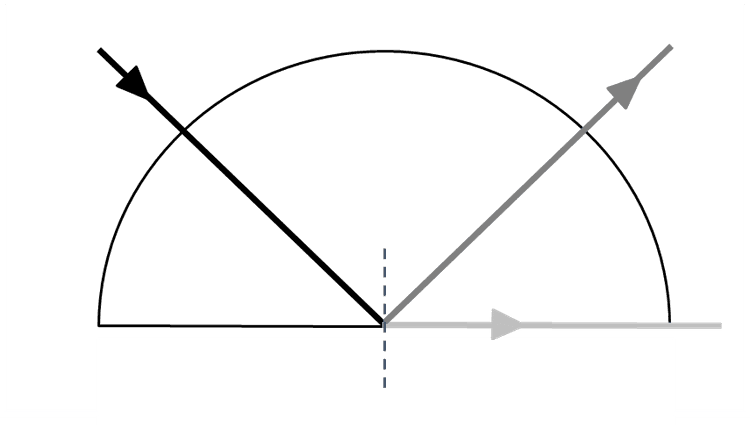
- At a boundary to a medium where the wave speed increases, waves are refracted away from the normal.
- If the angle of incidence is too big the waves will undergo total internal reflection.
- For a glass–air boundary, the total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is 42° or greater.
Keywords
Refraction - Refraction occurs when waves travel from one transparent medium to another, causing a change in direction.
Medium - A medium is the material through which a wave is travelling.
Angle of incidence - The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal.
Total internal reflection - Total internal reflection is when waves fully reflect from a boundary to a medium when greater wave speed, rather than being transmitted through.
Common misconception
Pupils sometimes rote-learn what specific examples of refraction look like, rather than developing a more general understanding of the direction waves turn based on changes in wave speed.
Teach pupils the general theory of refraction and apply it to a variety of different examples where wave speed changes (e.g. sound waves refract in the opposite direction to light at an air-glass boundary due to the different wave speeds).
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Refraction through a semicircular block, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 physics lesson on: Refraction through a semicircular block, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physics lessons from the Electromagnetic waves unit, dive into the full secondary physics curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions

reflected ray
refracted ray
incident ray
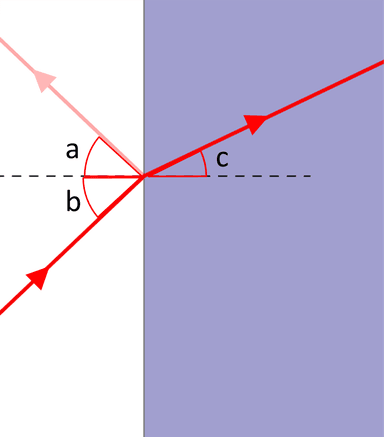
angle of reflection
angle of incidence
angle of refraction
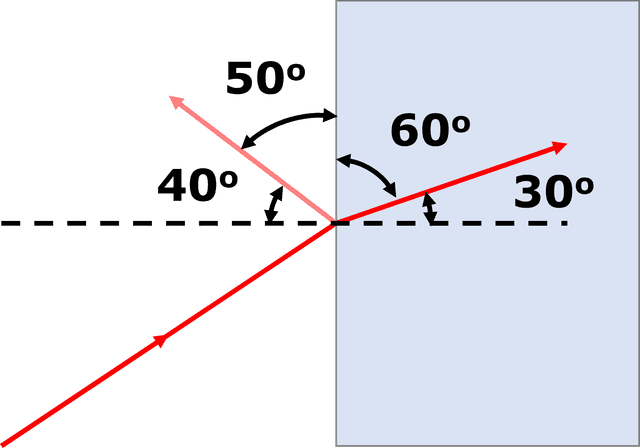
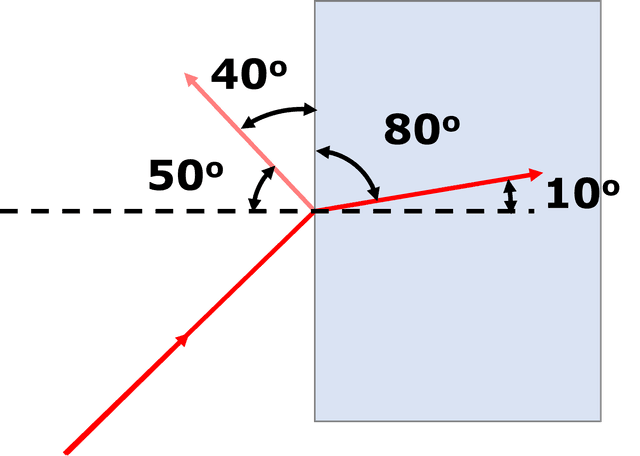
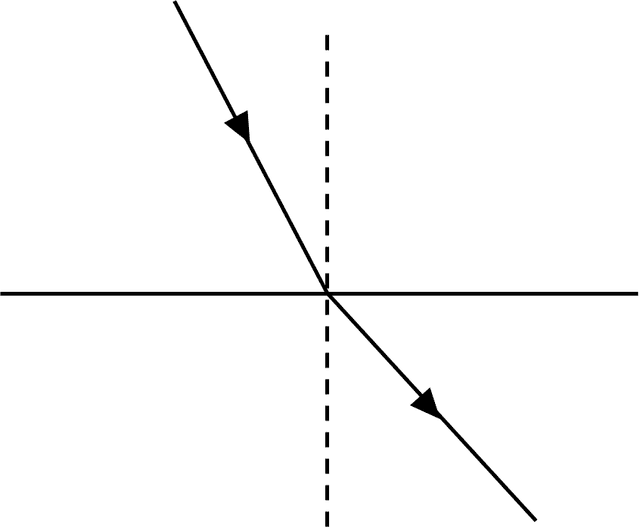
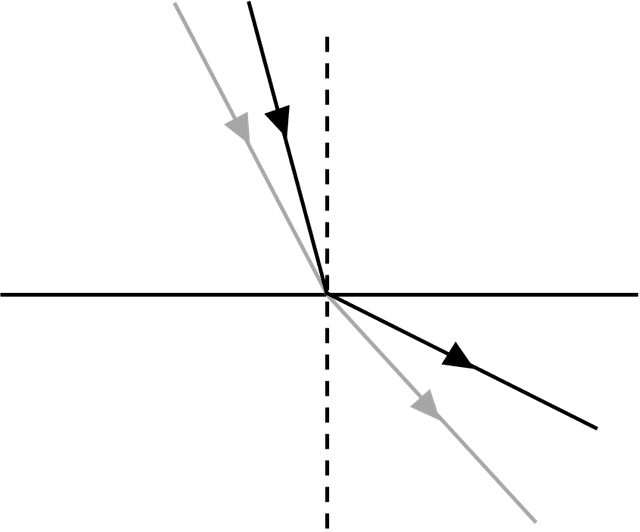
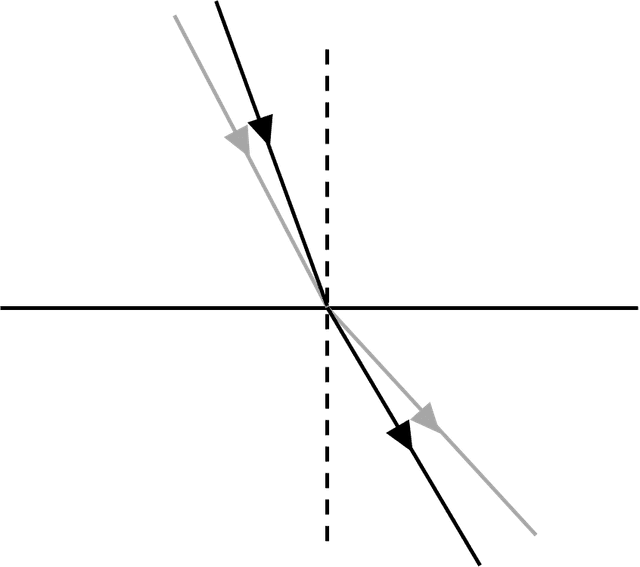
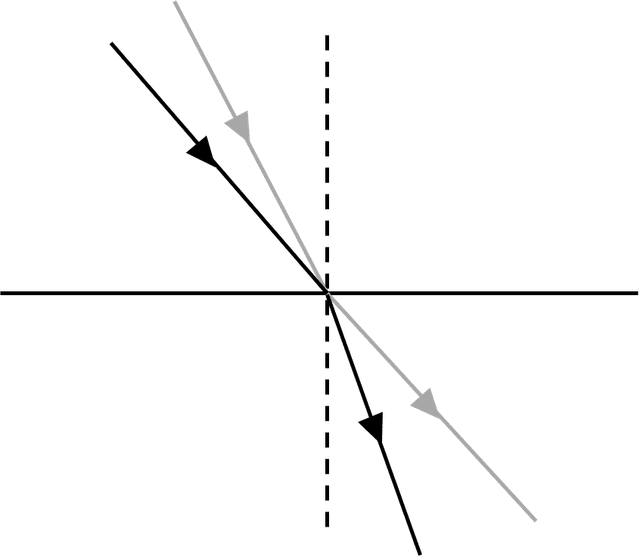
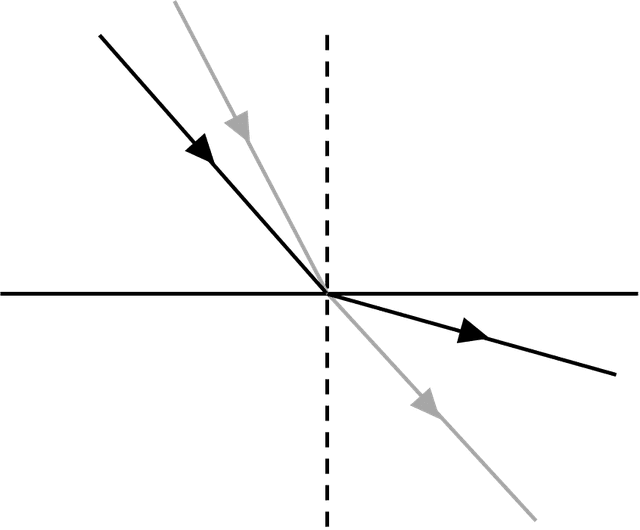
Exit quiz
6 Questions
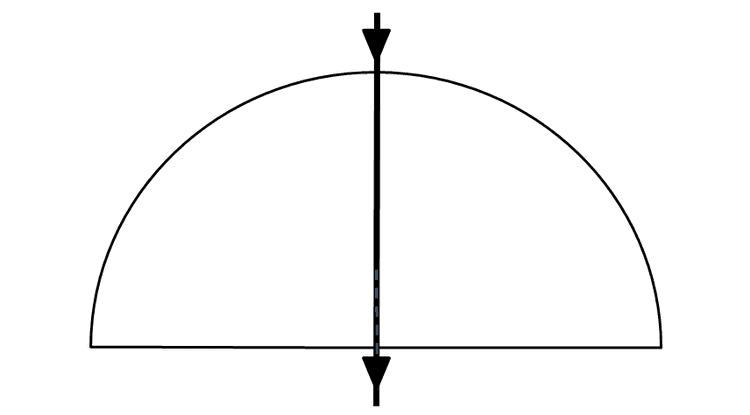
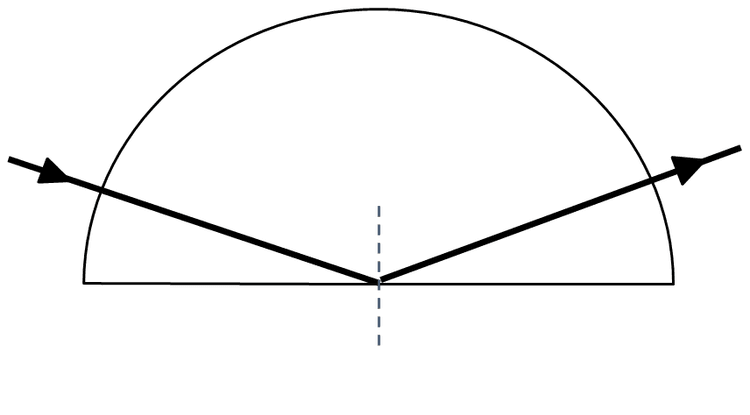




The beam passes through the boundary without refracting or reflecting.
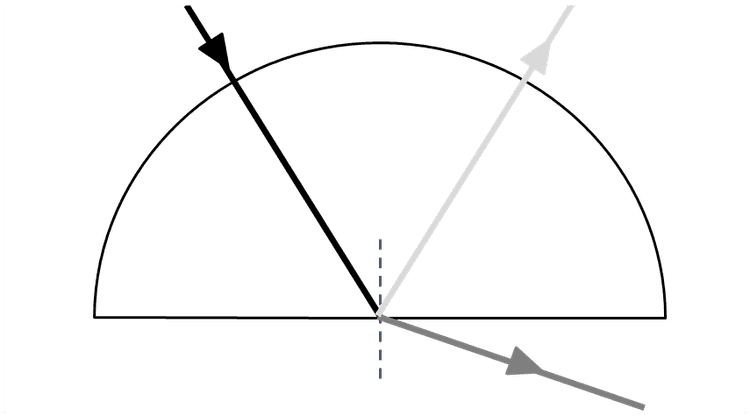
The refracted beam travels into the air.
The refracted beam travels along the boundary between water and air.
The beam is totally internally reflected (back into the water).


