Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 4
Generating and transporting electricity (non-statutory)
I can explain how electricity is generated and reaches our homes.
- Year 4
Generating and transporting electricity (non-statutory)
I can explain how electricity is generated and reaches our homes.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Traditional power stations burn coal or gas to generate electricity.
- Electricity is generated when the blades of a turbine turn causing a magnet to spin inside a coil of wire.
- Electricity is generated at traditional power stations or using the wind, water or the Sun.
- Electricity is transported around the country and to our homes through metal cables.
Keywords
Electricity - Electricity is needed for lighting, heating and making machines and appliances work.
Generate - To generate electricity is to produce it.
Power station - Electricity is generated at a power station.
Turbine - A turbine is a machine through which liquid or gas flows to turn a wheel.
Pylon - A pylon is a tall tower for carrying electricity cables high above the ground.
Common misconception
Electricity comes from the plug sockets in our homes. When electrical appliances are used, the electricity goes into them but is not part of a complete circuit.
Pupils will be taught where and how electricity is generated and how it is transported to our homes.
To help you plan your year 4 science lesson on: Generating and transporting electricity (non-statutory), download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 4 science lesson on: Generating and transporting electricity (non-statutory), download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 2 science lessons from the Simple electrical circuits unit, dive into the full primary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
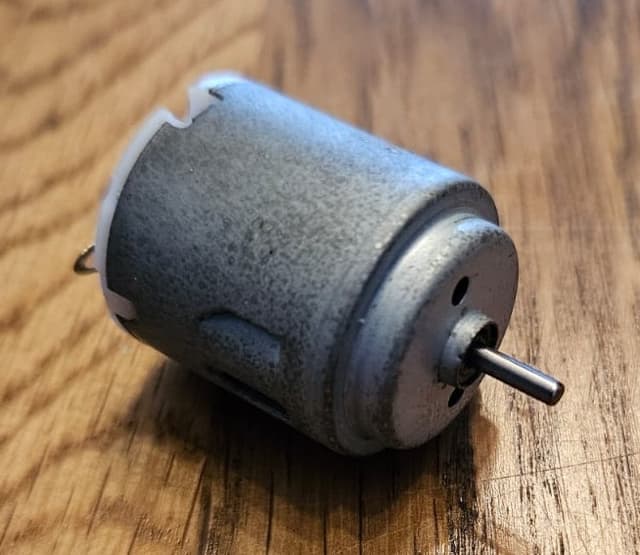
Q1.Which of the following is the name of the component shown?

Q2.Which of the following circuits is complete?
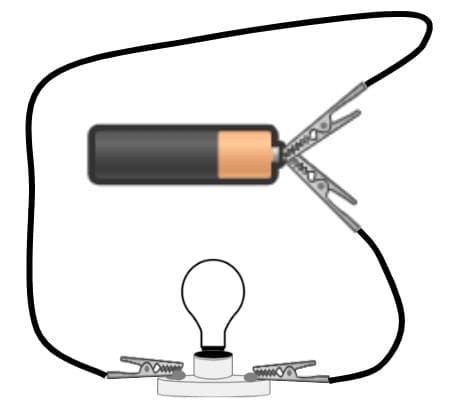
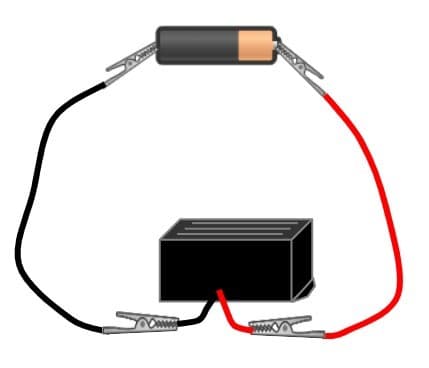

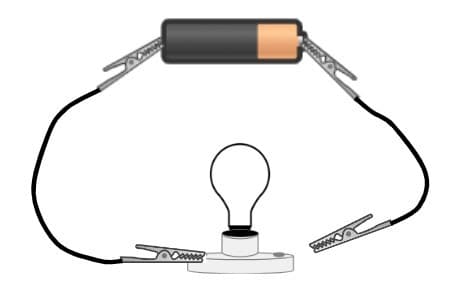
Q3.Match the following properties of a material to the product it would be used for.
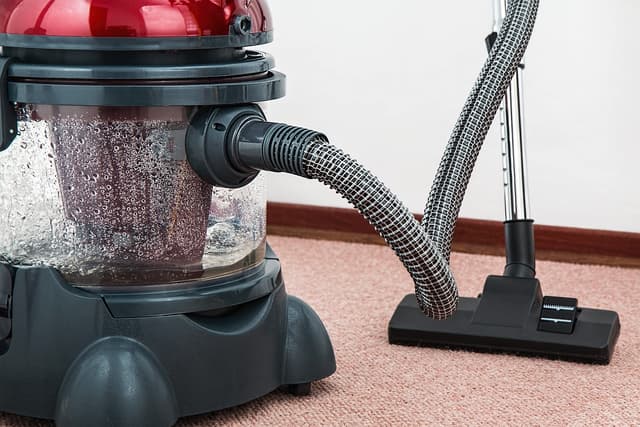

handle and casing on a vacuum cleaner
wiring of a vacuum cleaner


