Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Aerobic cellular respiration
I can describe the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration, and where it takes place.
- Year 9
Aerobic cellular respiration
I can describe the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration, and where it takes place.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Aerobic cellular respiration requires oxygen.
- The reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration can be summarised using a word equation.
- Aerobic cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria and cytoplasm of animal, plant and fungi cells.
- Cells that require more energy, because they do a lot of work, have more mitochondria.
Keywords
Aerobic cellular respiration - Aerobic cellular respiration is a chemical process that uses oxygen from the air and glucose to provide energy for life processes.
Oxygen - Oxygen is an element found in the air that is a gas at room temperature and a reactant in aerobic cellular respiration.
Carbon dioxide - Carbon dioxide is a compound made of carbon and oxygen that is a gas at room temperature and a product of aerobic cellular respiration.
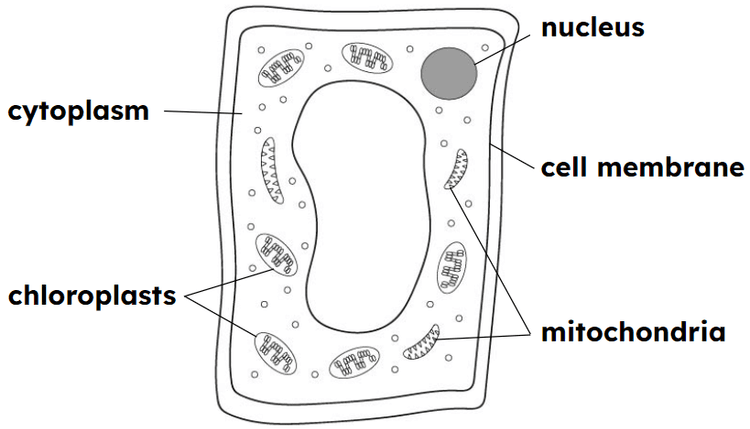
Mitochondria - Mitochondria are subcellular structures that use glucose and oxygen to carry out aerobic cellular respiration.
Cytoplasm - Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside a cell where its chemical reactions take place.
Common misconception
Aerobic cellular respiration is a single chemical reaction.
This lesson uses the terms 'chemical process' and 'series of chemical reactions'.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Aerobic cellular respiration, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Aerobic cellular respiration, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Breathing and respiration unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Living organisms undergo cellular respiration to provide for life processes.
Q2.True or false? Respiration takes place all of the time.
Q3.Who’s right?



Q4.True or false? Glucose can be described as a fuel.
Q5.True or false? Breathing and cellular respiration are the same thing.
Q6.Match the process to its description.
A mechanical process not involving chemical reactions.
Chemical reactions that take place to provide energy.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Complete the word summary for cellular respiration; glucose + → carbon dioxide and water.
Q2.Where does respiration take place in fungi, plants and animals?
Q3.Match the substances to the description of their role in cellular respiration.
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
Q4.Where do plants obtain glucose from?



