Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 7
DNA from fruit
I can observe DNA extracted from fruit and identify the main apparatus and steps in the extraction method.
- Year 7
DNA from fruit
I can observe DNA extracted from fruit and identify the main apparatus and steps in the extraction method.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- DNA is a chemical substance that can be extracted from the cells of organisms such as fruit.
- DNA molecules cannot usually be seen with the unaided eye, but clumps of it can be seen when a lot of it is extracted.
- Observing or following an appropriate method to extract DNA from fruit (e.g. kiwi fruit).
- Discussion of apparatus and techniques used to filter the tissue and extract the DNA.
- Observing and describing the appearance of the DNA after extraction.
Keywords
Cell - A cell is the smallest living building block of an organism, and it contains genetic material that provides the instructions used to build and control the organism.
DNA - Genetic material is made of a chemical substance called DNA, in which the instructions are stored using the genetic code.
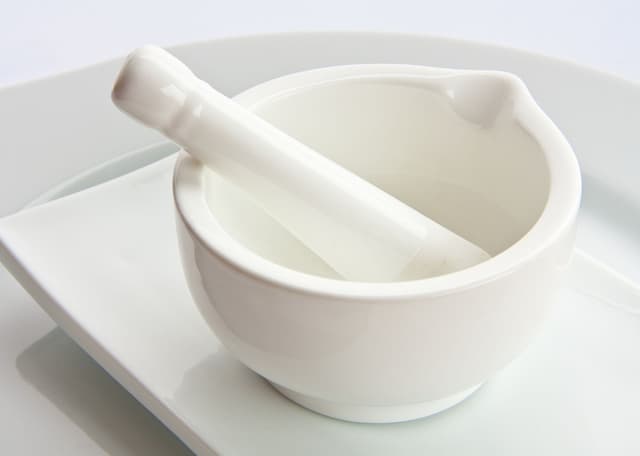
Mortar and pestle - A mortar and pestle are used to crush and grind up solid samples.
Filter - To filter a mixture is to separate out insoluble particles from a liquid. It can be done using a funnel and filter paper.
Pipette - A pipette is used to transfer small quantities of liquid.
Common misconception
DNA is just 'genetic information' and not a substance; not all organisms contain DNA (e.g. plants).
The lesson demonstrates that DNA is a physical, chemical substance that can be extracted from cells, and shows that plants contain DNA.
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: DNA from fruit, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: DNA from fruit, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Heredity and DNA unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.DNA is stored in which part of an animal, plant and fungi cell?
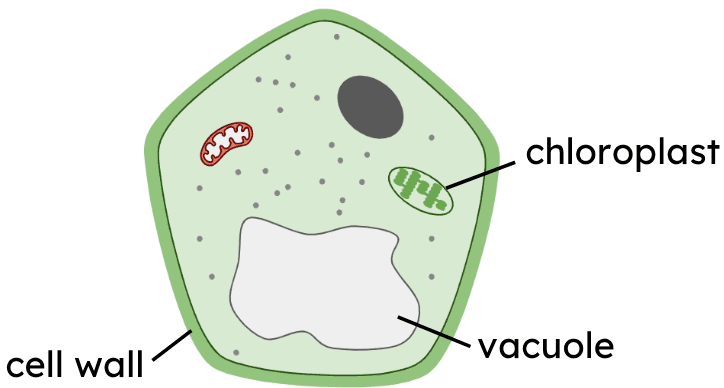
Q2.What type of cell is shown in this image?
Q3.What is the name of the chemical molecule which stores genetic information?
Q4.Why can't we usually see DNA molecules with our eyes?
Q5.Which of these words describes the equipment that is used in practical science investigations?
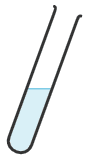
Q6.What is this piece of apparatus called?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is the name of this chemical molecule?

Q2.Match the step from the DNA extraction method to its role.
releases cells from the tissue
removes large pieces such as seeds
to add a small amount of salt
Q3.Name this piece of apparatus.

Q4.Match the chemical name to its job in the DNA extraction investigation.
unwinds the DNA
breaks down cell membranes
DNA floats in it and forms clumps


