Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Hooke's law
I can describe and explain the relationship between the extension of a spring and the force stretching it.
- Year 9
Hooke's law
I can describe and explain the relationship between the extension of a spring and the force stretching it.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A line of best fit can show the relationship between variables clearly.
- The extension of a spring increases the same amount for each equal sized increase in force.
- The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied.
- A spring is elastic because it returns to its original length when a force is removed.
- Hooke's law describes the behaviour of springs.
Keywords
Line of best fit - A line of best fit passes between a set of data points on a graph to show the pattern.
Directly proportional - Variables are directly proportional when one is a constant multiple of the other.
Elastic - A spring is elastic when it returns to its original length after forces are removed from it.
Hooke's law - Hooke's law describes the behaviour of a spring when it is stretched.
Common misconception
The line of a graph must go through all of the points.
Get pupils to invent plots to add to a graph showing a line of best fit that include small mistakes in the measurements.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Hooke's law, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Hooke's law, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Hidden forces unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Complete the statement. The word used to describe the force on an object due to a gravitational field is ...
Q2.A pupil puts different forces on a spring. Starting with the smallest extension, sort the forces into order of the extension they cause.
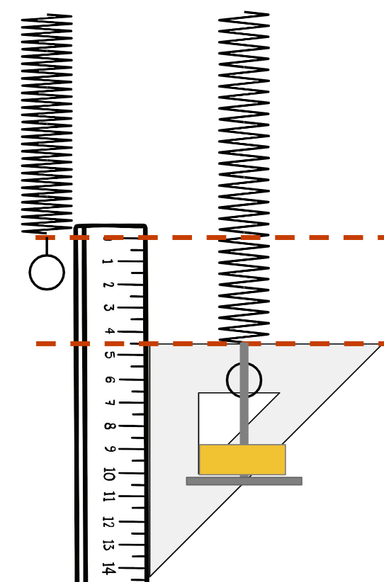
Q3.The figure shows a spring before and after a weight has been added. What is the extension of the spring when the mass is placed on it?
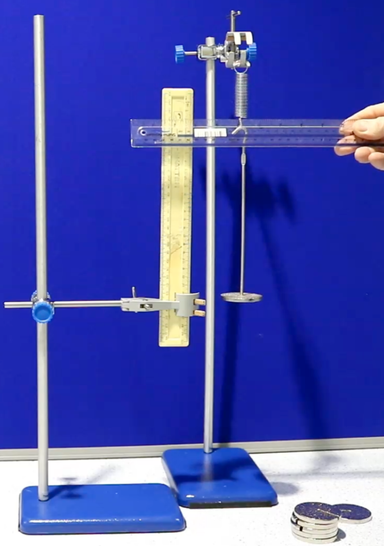
Q4.The photograph shows a pupil measuring the extension of a spring. How could the pupil improve the accuracy of the measurement?
Q5.The gravitational field strength on Earth is 10 N/kg. What size mass will have a weight of 1 N?
Q6.Why is it important to measure the extension of a spring when masses are taken off as well as being added?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the key word or phrase to the definition.
Passes between data points on a graph to show the pattern.
When one variable doubles, the other is doubled.
Returns to its original length when the forces are removed.
A description of the behaviour of springs.
Q2.Which statement about springs is correct when they are stretched?
Q3.What happens to the extension of a spring if the force acting on it is increased from 6 N to 18 N?
Q4.Which of the following describes the line of best fit for a graph where the two variables are directly proportional?
Q5.Some pupils add too much force to a spring. For each extra 1 N they then add, the extension increases much more than expected. What will happen to the spring when the force is removed.
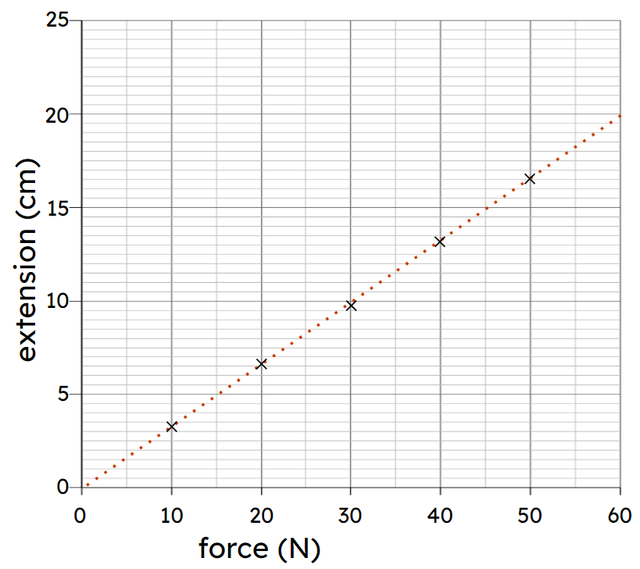
Q6.The graph shows the extension of a spring for different forces acting on it. What is the extension per newton for this spring? Give your answer to two significant figures.