Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Using electromagets
I can describe how electromagnets are used in cranes, locks, bells and motors.
- Year 9
Using electromagets
I can describe how electromagnets are used in cranes, locks, bells and motors.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
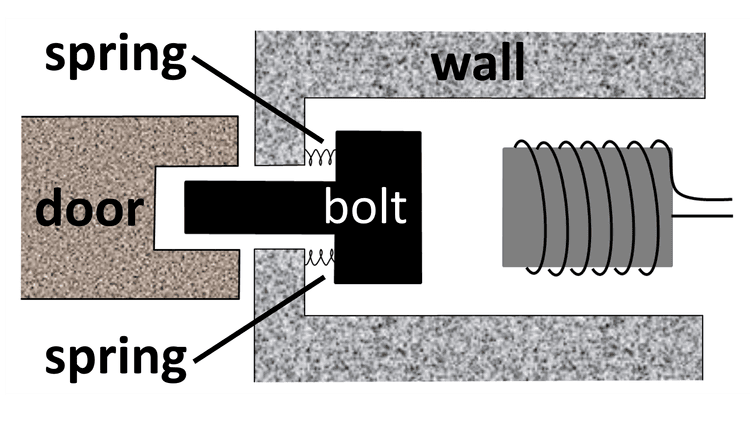
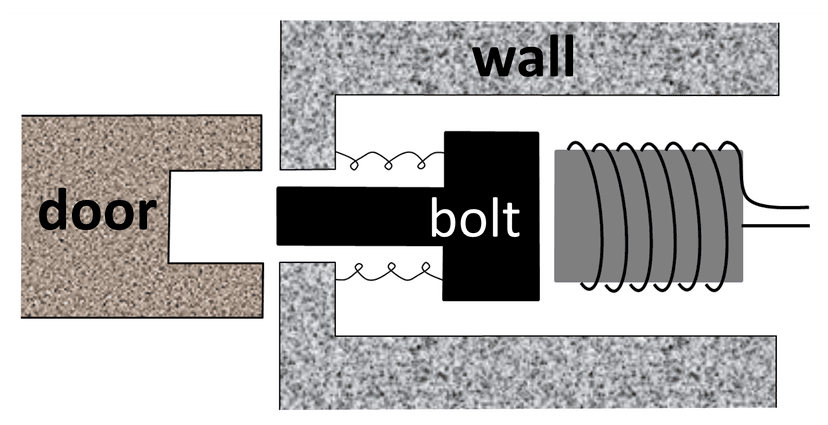
- An electromagnetic door lock uses an electromagnet to pull a magnetic bolt to unlock a door.
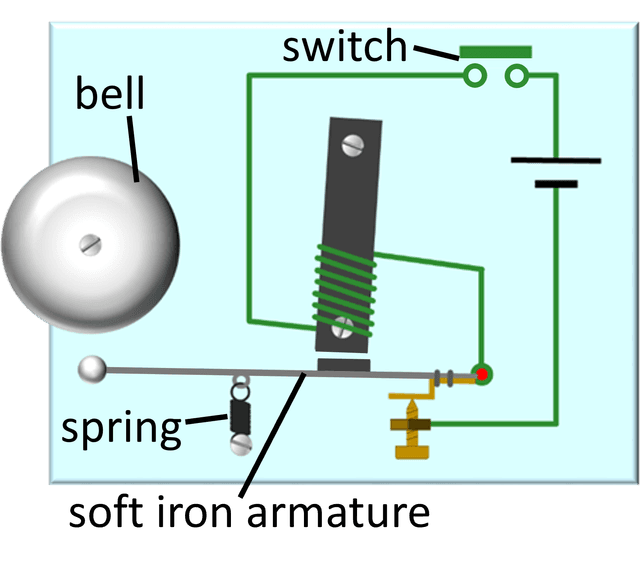
- An electric bell often contains an electromagnet that attracts and moves the striker, making it hit the bell.
- As an electromagnet moves the striker in an electric bell, it breaks its own circuit to let the striker spring back.
- A motor contains a spinning coil of wire that is an electromagnet.
- When there is a current in the spinning coil of wire in a motor, other magnets around it will push it round.
Keywords
Electromagnet - A magnet made by running current through a coil of wire round an iron core.
Temporary magnet - An electromagnet that loses its magnetism when current stops flowing through it.
Electric lock - A lock that can be opened with an electromagnet when a switch is closed.
Electric bell - A bell that uses an electromagnet to strike a clapper on the bell and which resets itself to keep ringing.
Electric motor - A motor that uses a magnetic field to produce a force.
Common misconception
It is very common for pupils to think that uninsulated wire is needed for the coil of an electromagnet.
When discussing an electromagnet, always refer to the insulated wire in its core, which is necessary so the current in each turn adds to the strength of the electromagnet.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Using electromagets, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Using electromagets, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Magnets and electromagnets unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Insulated wire, AAA battery, 2 safety pins, insulating tape, neodymium magnet and sandpaper.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.An object that always behaves as a magnet is called a __________ magnet.
Q2.Which of the following objects would be attracted to an electromagnet?
Q3.Which of the following statements explain why soft iron is usually used for the core of an electromagnet?
Q4.Which of the following is a definition of a complete circuit?
Q5.A pupil has a coil of wire coated in yellow plastic, as shown. They attach metal clips to the ends of the coil and connect them to a suitable battery. Why is there no magnetic field around the coil?
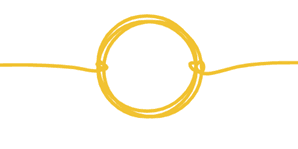
Q6.A pupil experiments with a bar magnet and an electromagnet. Which of the following statements are correct?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.An electromagnet that loses its magnetism when current stops flowing can also be called a __________ magnet.
Q2.A scrapyard uses an electromagnet to move objects made of a magnetic material such as steel. Which of the following describe an advantage of using an electromagnet compared with a permanent magnet?
Q3.Which of the following is the purpose of the springs attached to the bolt of the electromagnetic door lock shown?
Q4.The diagram shows an electric door lock. Which of the following statements are correct?
Q5.The diagram shows an electric bell. Which of the following happen as the switch is pressed?