Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Structure of polymers
I can give examples of polymers and explain how the properties of polymers depend on their structure.
- Year 9
Structure of polymers
I can give examples of polymers and explain how the properties of polymers depend on their structure.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Polymers are made from small molecules called monomers that join together to form very long chains of atoms.
- Some polymers have high melting points because their molecules are hard to separate.
- Polymers can be made synthetically, but some also exist naturally.
- A plasticiser added to a polymer gets between polymer molecules and allows them to move over each other more easily.
- Cross-links between polymer molecules can make a polymer harder and less flexible.
Keywords
Polymer - Long-chained molecules formed by joining together monomers.
Forces of attraction - A pulling force that keeps particles close together.
Synthetic - A product that is manufactured from natural resources.
Plasticiser - A substance that is added to a polymer to increase its flexibility.
Cross-link - A chemical bond between different chains of atoms in a polymer.
Common misconception
Students often think that intermolecular forces exist within a molecule, unaware of the significant difference in strength between chemical bonds within atoms and the forces between molecules.
Help students to make the link between the structure of the polymer and its property by using models. Point out where the intermolecular forces occur and compare this to where the chemical bonds are.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Structure of polymers, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Structure of polymers, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Materials unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following three properties make polymers useful for making plastic water bottles?
Q2.Plastics are polymers, but not all polymers are plastics. Which of the following materials are classified as polymers?
Q3.Models are used in science to test ideas without facing practical or ethical issues. However, they have , such as only representing one aspect of a concept rather than the whole.
Q4.Match the following key terms to their definition.
particles that make up chemical elements
a strong force that holds atoms together in a compound
a substance where two or more different elements are chemically bonded
a substance made up of only one type of atom
made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded (usually non–metals)
Q5.Which of the following properties of rubber makes it useful for making rubber bands?
Q6.Consider ice, water, and water vapour. The atoms and molecules are held together differently and with varying strengths. What happens at the boiling point when water turns to water vapour?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following key terms to their definition.
a strong force that holds atoms together in a compound
a chemical bond between atoms in different polymer chains
a pulling force that keeps particles close together
a substance that is added to a polymer to increase its flexibility
Q2.Materials can be natural or synthetic. Natural means they occur in nature. Synthetic means they are .
Q3.Polymers can be represented with models. Which list correctly describes the image with three polymer models, from left to right?
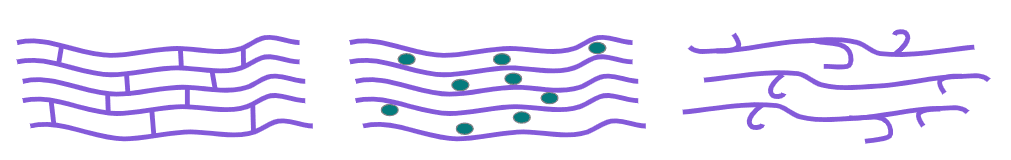
Q4.Match the following key terms to their description.
natural; carbohydrate found in plant cell walls
natural; nucleic acid involved in carrying genetic information
synthetic; high density poly(ethene) used for plastic bottles
synthetic; low density poly(ethene) used for plastic bags
synthetic; poly(vinyl chloride) used for sockets, switches and wellies
natural; protein fibre often made by sheep


