Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 8
Newton's First Law
I can describe and explain how a resultant force can change the movement of objects.
- Year 8
Newton's First Law
I can describe and explain how a resultant force can change the movement of objects.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Resultant forces make the movement of things change.
- Friction acts against the direction of movement of an object.
- An object will continue to move at a steady speed in a straight line unless a resultant force is acting.
Keywords
Stationary - A stationary object is not moving.
Resultant force - A resultant forces the sum of all forces acting on an object.
Frictional force - Frictional forces act between surfaces, to oppose the movement of an object.
Gravitational force - The gravitational force on an object pulls it downwards, towards Earth.
Common misconception
Pupils believe driving forces are needed to keep objects moving at constant speed.
Demonstrate that friction (and drag) bring objects to a stop, showing that different surfaces produce the forces that slow objects.
To help you plan your year 8 science lesson on: Newton's First Law, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 8 science lesson on: Newton's First Law, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Moving by force unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What can make an object speed up, slow down, change direction or change shape?
Q2.What is the name of the force which is produced when two solid surfaces rub against each other?
Q3.What is the name of the force that opposes movement when a solid object passes through a liquid or gas?
Q4.A firework has a weight of 0.2 N and it produces an upwards thrust of 1.0 N when launched. What it the resultant force on the firework?
Q5.Someone pushes a trolley along a flat road until it is moving quickly. They then jump on for a ride, putting both their feet up. Which of these statements is correct after they are on the trolley?
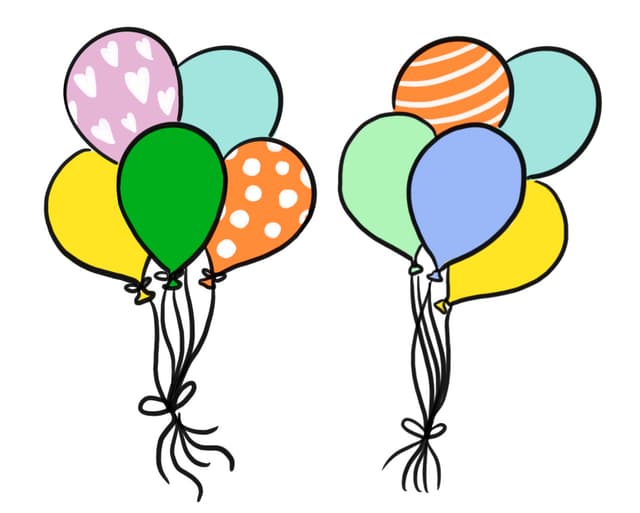
Q6.A child lets go of a bundle of ten large helium balloons, each has a weight of 0.5 N. Each balloon produces an upthrust of 1 N. What is resultant force on the bundle of balloons?

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the key word to the definition.
not moving
force between two surfaces in contact when one tries to move
the sum of the forces on an object accounting for direction
a force that pulls objects towards Earth
a change in speed or direction of movement
Q2.Which of these is an example of an object that has no propelling (forwards acting) force?
Q3.Which of these are true when there is no resultant force acting on an object?
Q4.The figure shows two forces acting on a lorry. What is the resultant force on the lorry?

Q5.The figure shows two forces acting on a moving lorry. What will happen to the lorry?

Q6.A bowling ball is launched from a ramp along a bowling alley as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements are true?



