Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Seed dispersal: practical
I can explain why it is important for a plant that its seeds are dispersed over a wide area, and carry out an experiment to measure seed dispersal.
- Year 9
Seed dispersal: practical
I can explain why it is important for a plant that its seeds are dispersed over a wide area, and carry out an experiment to measure seed dispersal.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Seeds are dispersed by different mechanisms to increase the chance of survival.
- Seeds are adapted to match the mechanism for dispersal; e.g. wind dispersed are light with a large surface area.
- Variables are factors that affect the process being investigated, the dependant variable is distance the seed travels.
- Practical investigation of how far model seeds disperse with changes to their template.
- Repeat measurements for each value to identify anomalous results and calculate a mean.
Keywords
Seed dispersal - Mechanism by which seeds are transported away from the parent plant.
Adaptations - Features of living organisms that help them survive in their environment.
Variable - Anything that can change or be changed in an investigation.
Repeats - Measurements of the same value allows anomalous results to be identified.
Mean - A measure of average where all values are added together and divided by the number of repeat measurements that have been taken.
Common misconception
That means are always divide by three.
Show examples where the number of repeats varies.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Seed dispersal: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Seed dispersal: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Reproduction in plants unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
See additional materials.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.True or false? Seeds are the offspring produced from sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
Q2.What are the three main parts of a seed?

Q3.Calculate the mean of the following numbers: 10, 5 and 15.
Q4.What is a factor that might affect the process that is being investigated?
Q5.Match the type of variable to its description.
variables that are chosen to be changed
variables that are measured
variables that are kept the same
Q6.What is the most likely dispersal mechanism for sycamore seeds?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is the mechanism by which seeds are transported away from the parent plant called?
Q2.Match the seed to its dispersal mechanism.

Q3.Results that don't fit the pattern are called results.
Q4.Calculate the mean of the following results.
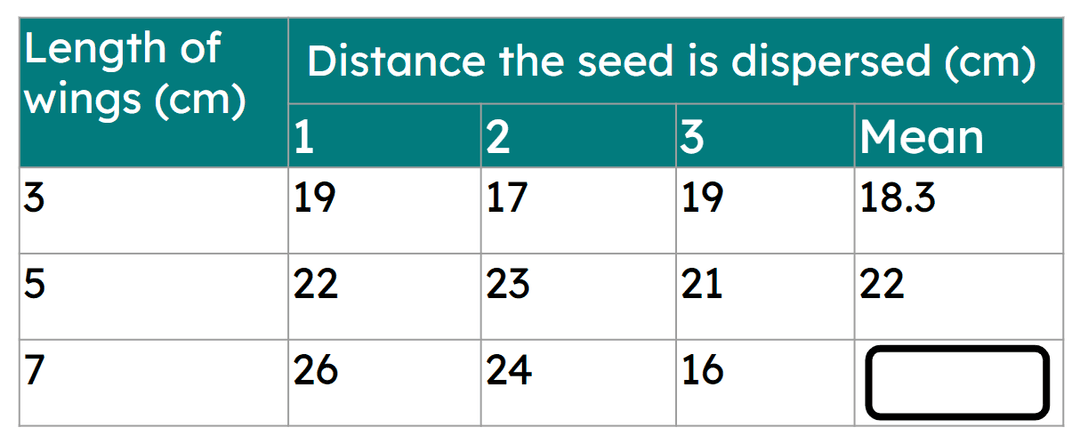
Q5.Match the variables to their description for an investigation into how wing width affects the distance a seed travels.
width of wings
distance the seed travels
length of wings


