Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 9
Thickness of a wire
I can describe how a battery pushes current through wires of different thicknesses.
- Year 9
Thickness of a wire
I can describe how a battery pushes current through wires of different thicknesses.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The thicker a wire, the smaller its resistance.
- The greater the cross–sectional area of a wire, the smaller its resistance.
- Electric current in a wire is a flow of electrons moving between ‘atoms’ (metal ions).
- Doubling the cross-sectional area of a wire halves its resistance.
- Doubling the cross-sectional area of a wire doubles the number of electrons that can flow through the wire.
Keywords
Atom - An atom is the smallest particle of a chemical element that exists.
Electron - Electrons are the charges in conductors that flow to give an electric current.
Metal ion - A metal ion is formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons and has a positive charge.
Resistance - Resistance is a measure of how hard it is for current to flow.
Proportional - Two variables are proportional if one changes as a multiple of the other.
Common misconception
Many pupils are likely to still use the terms current, voltage and resistance interchangeably.
Repeatedly question pupils about each term and challenge them to use each one correctly throughout their explanations, both written and verbal.
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Thickness of a wire, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 9 science lesson on: Thickness of a wire, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Resistance and parallel circuits unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
A range of samples of constantan (or nichrome) wire, SWG 30-40, metre rules, crocodile clips, electrical leads, ammeters capable of measuring current in milliamps, 3V batteries, wire cutters.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which two of the following statements about electricity are correct?
Q2.In a fair test, the variable(s) that need to be kept the same are called ...
Q3.Which of the following will happen if another battery is added (correctly aligned and in series) to the circuit shown?
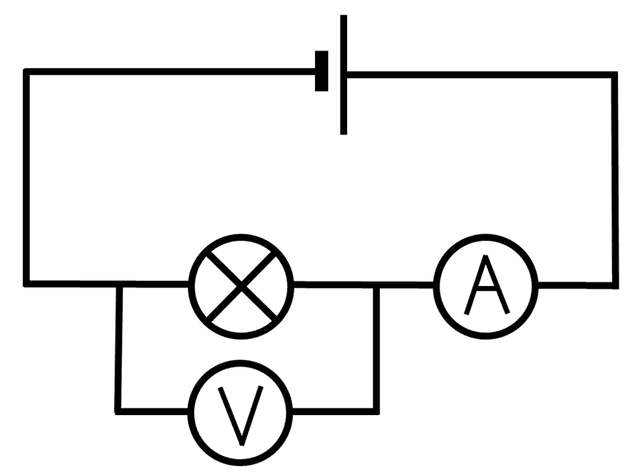
Q4.Which of the following will happen if two identical batteries are connected in series with a lamp, but aligned in opposite directions?
Q5.Which of the following resistors will oppose the flow of current the most?
Q6.Which of the following will happen if a resistor in a series circuit is moved closer to the battery?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which two of the following statements explain what will happen to a metal atom when it loses an electron?
Q2.Which two of the following metals are the best conductors of electricity?
Q3.Which of the following statements explain why a thinner metal wire has a higher resistance than a thicker one, per metre?
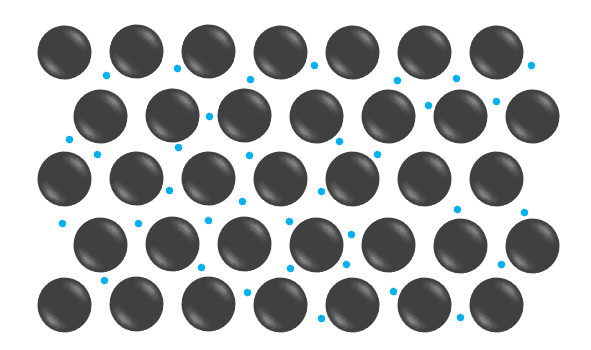
Q4.The image shown is a representation of the arrangement of the particles in a metal.
Which of the following particles do the small, blue spheres represent?