Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 7
Gravity
I can describe the effects of gravity acting towards the centre of a nearby planet, moon or star.
- Year 7
Gravity
I can describe the effects of gravity acting towards the centre of a nearby planet, moon or star.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
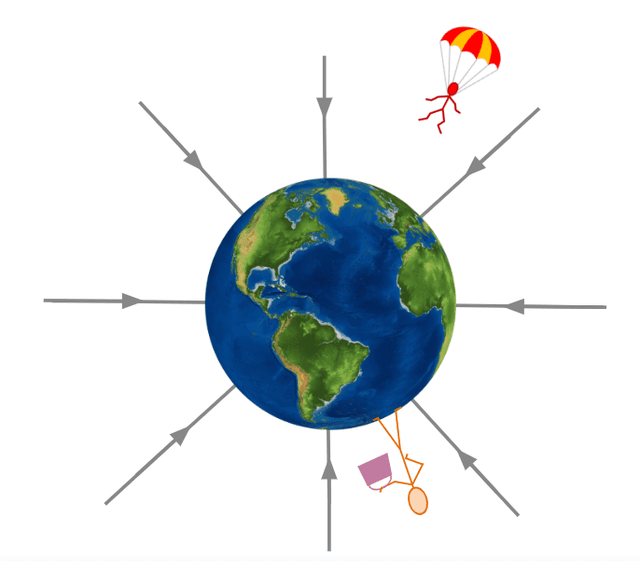
- Gravitational forces pull (attract) objects towards the centre of large objects like planets, moons and stars.
- The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravity.
- The gravity of a planet, moon or star extends far into space, but gets weaker with distance.
- Earth’s gravity pulls the Moon towards the centre of Earth, changing the Moon's direction, making it orbit around Earth.
- The Sun's gravity pulls Earth towards the centre of the Sun, changing Earth's direction, making it orbit around the Sun.
Keywords
Gravitational force - Gravitational forces pull objects towards large objects like planets, moons and stars.
Attraction - An attraction is a force that acts to pull one object towards another.
Orbit - An orbit is the movement of one object in a loop around another object.
Common misconception
There is no gravity in space, even a short distance from the Earth.
Carefully whirl a rubber bung around your head on a length of string to show how force of a string keeps it orbiting in a circle, just as the force of gravity keeps the Moon orbiting the Earth and the planets orbiting the Sun.
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Gravity, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Gravity, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Our solar system and beyond unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is the name of the force that pulls objects towards the ground?
Q2.In which direction will a ball move if you pick it up and then release it above the ground?
Q3.Which scientist is thought to have discovered the existence of gravity after seeing an apple fall from a tree in their garden?
Q4.Where would you feel the strongest gravitational force of attraction from Earth?
Q5.Which planet has the strongest gravitational field?
Q6.Put these pairs of orbiting objects in order of increasing gravitational force between them, starting with the smallest.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of these statements about the gravitational force from one object acting on another is correct?
Q2.Why does the person shown on the southern hemisphere of Earth not fall off?
Q3.Put these objects in order of increasing gravitational field strength, starting with the smallest.
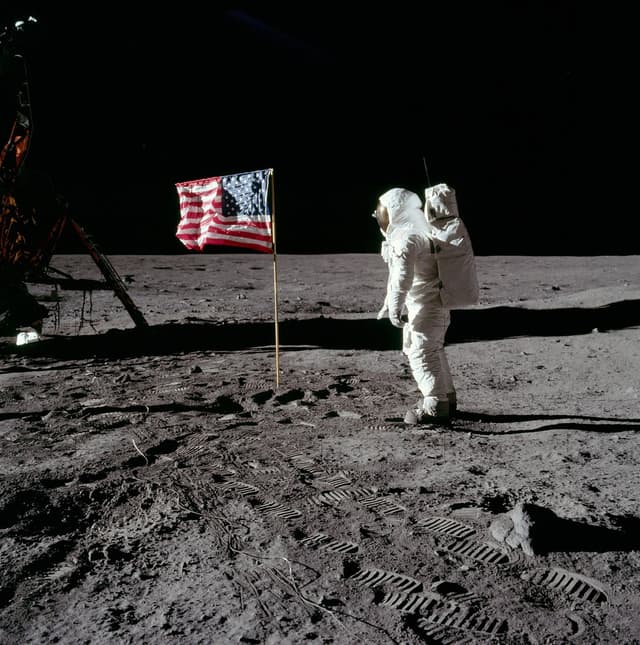
Q4.The photo shows an astronaut on the Moon with a flag. Why does the flag not droop towards the surface of the Moon?



