Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 7
Seasons on Earth
I can explain how and why the seasons change, and why some countries do not have summers and winters.
- Year 7
Seasons on Earth
I can explain how and why the seasons change, and why some countries do not have summers and winters.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
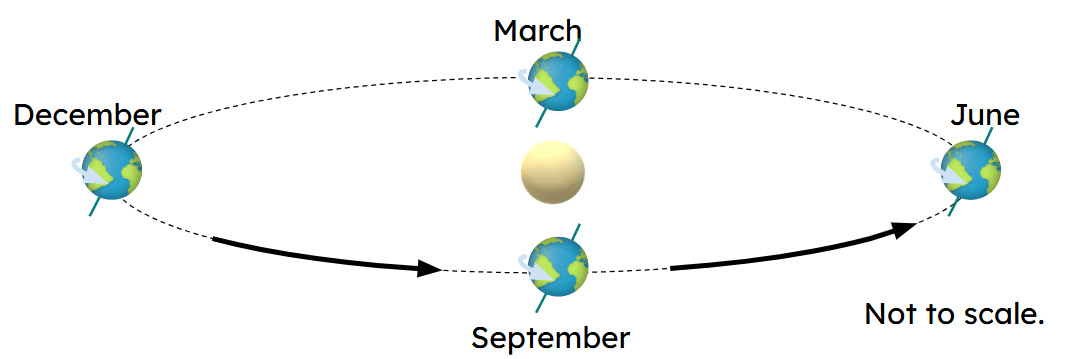
- The seasons change because of Earth’s tilted axis, which does not change direction as Earth orbits the Sun.
- In June, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun so has summer, and the southern hemisphere has winter.
- In December, the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun so has winter, and the southern hemisphere has summer.
- The seasons that occur at a place on Earth can be explained by the different angles made to the sun's rays over a year.
- Countries near the Equator do not experience summers and winters as they stay close to ‘face-on’ to the Sun all year.
Keywords
Summer - Summer is the warmest season, when the Sun is highest in the sky and there are more hours of daylight.
Winter - Winter is the coldest season, when the Sun is lowest in the sky and there are fewer hours of daylight.
Hemisphere - A hemisphere is half a sphere.
Tilt - Something is tilted if it is at an angle to the horizontal or vertical.
Orbit - An orbit is the path one object takes around another object.
Common misconception
The seasons are caused by Earth moving closer or further from the Sun, the Sun being hotter or colder, or Earth's tilt changing as it orbits the Sun.
Remind pupils that the Sun's output is constant and also that there is strong evidence for Earth's orbit of the Sun being almost a perfect circle. Seasonal change happens because the direction of Earth's tilt doesn't change as it orbits the Sun.
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Seasons on Earth, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Seasons on Earth, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Our solar system and beyond unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.When it is winter in northern Europe, what season is it in South Africa?
Q2.What angle is Earth titled at compared with the plane of its orbit?
Q3.Which season has the longest days?
Q4.What place on Earth experiences 24 hours of daylight on 25th December?
Q5.Which places on Earth get the most light from the Sun?
Q6.A child living in York is writing out their address for an alien. Put the places in correct order, starting with the city.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
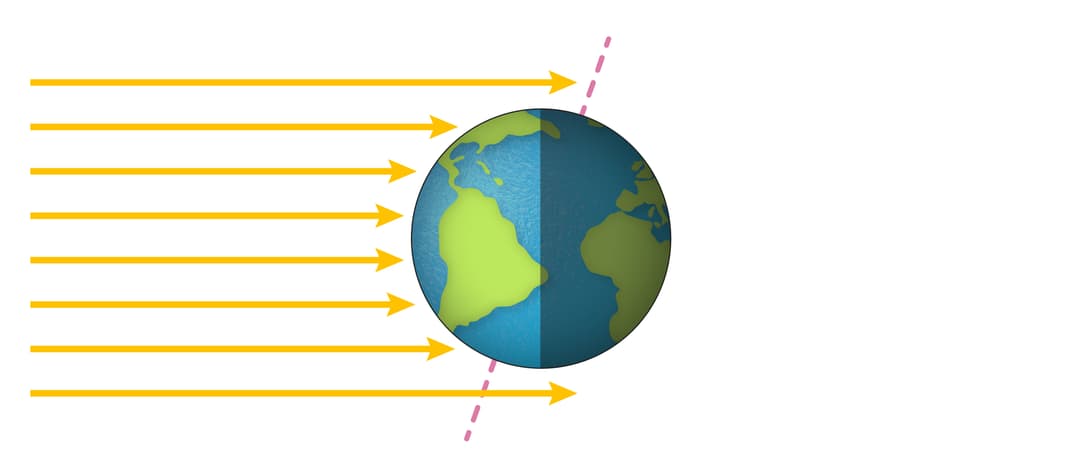
Q1.The dashed red line in the picture represents Earth's tilted of rotation.
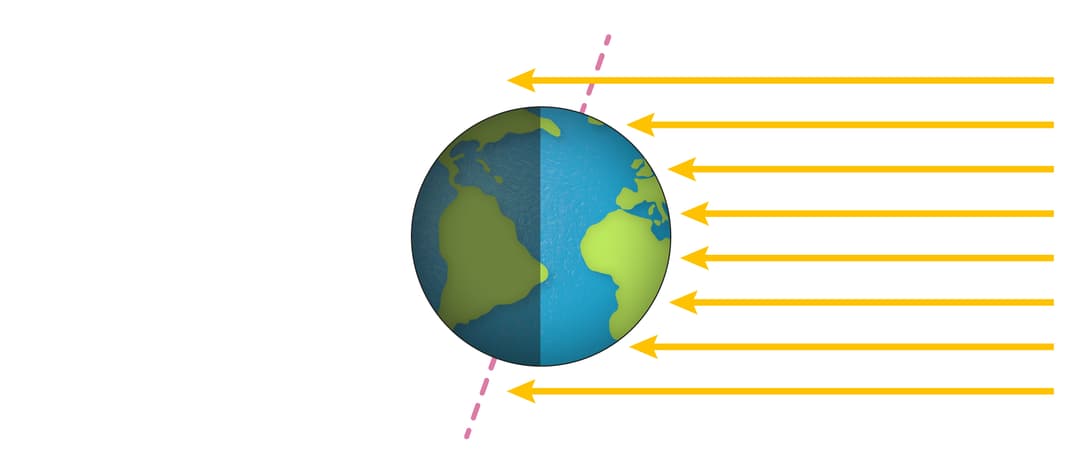
Q2.In countries that have summers and winters, the seasons change because Earth’s tilted axis does not change as Earth orbits the Sun.
Q3.Which image best represents Earth's orbit of the Sun?
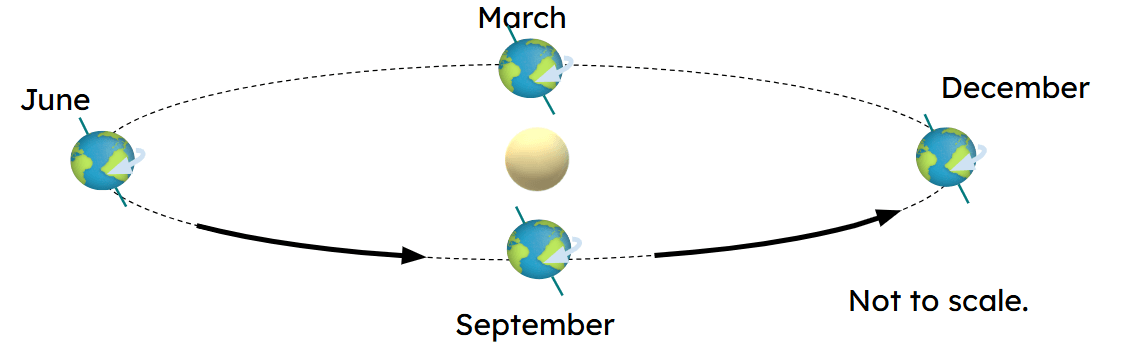
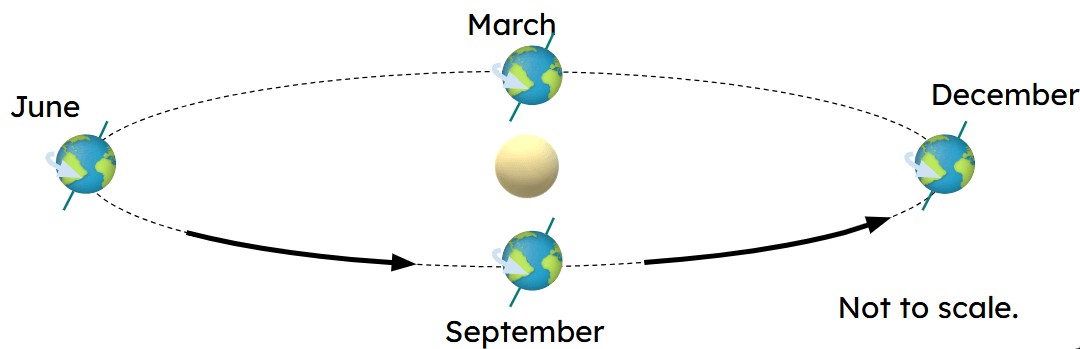
Q4.Which statement about places at the equator is true?
Q5.Which month is represented in this image, and why? The pink lines are the paths of the UK and southern Chile as Earth spins. The yellow arrows are the Sun's rays.