Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 7
- Year 7
Pure substances
I can describe the difference between a pure substance and a mixture.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A pure material is made of only one type of substance
- A pure material has a fixed melting point and boiling point
- Impurities change the melting and boiling point of a material
- A mixture contains two or more types of substances which can be easily separated
- Mixtures melt or boil over a range of temperatures
Keywords
Pure substance - A pure substance contains only one type of chemical
Mixture - A mixture is a material that contains two or more different substances which can be physically separated
Impurity - An impurity is a chemical that is found in a material in very small amounts, but can change the material's properties
Common misconception
Pupils mistake common (everyday) usage of pure (i.e. 'pure orange juice) as being a pure substance
'Everyday' usage refers to one *source* whereas scientific usage refers to particle composition. Take particular care when discussing water.
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Pure substances, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Pure substances, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Solutions unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
See additional materials.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - chemicals
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The three states of matter are: solid, , and gas.
Q2.Which of the following are examples of materials in the solid state at room temperature?
Q3.All matter is made up of .
Q4.Match the state of matter with the correct particle diagram.
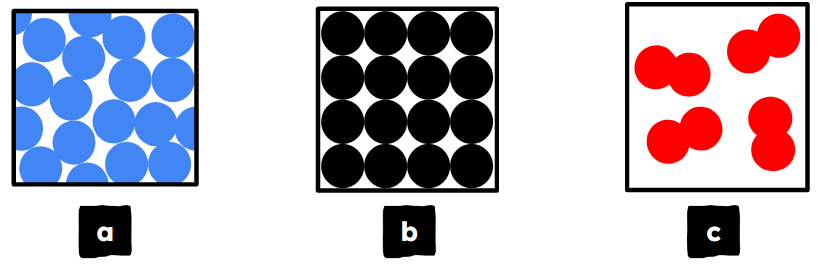
liquid
solid
gas
Q5.Which description correctly describes a substance's melting point?
Q6.What properties would you expect of a material with this particle arrangement?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A material is composed of only one type of chemical.
Q2.Which of the following is an example of a pure substance?
Q3.What is the name given to a substance found in a material in very small amounts, but which can alter the material's properties?
Q4.Complete this sentence: A significant feature of a mixture is that it...
Q5.Which diagram correctly represents a mixture in the solid state?