Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 7
Reflecting light from mirrors
I can investigate the reflection of light from mirrors by tracing beams of light and measuring angles, and compare results to the known laws of reflection.
- Year 7
Reflecting light from mirrors
I can investigate the reflection of light from mirrors by tracing beams of light and measuring angles, and compare results to the known laws of reflection.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Light travelling in one direction (along a ray) that hits a mirror reflects (bounces off the mirror) in one direction.
- The ‘normal’ is an imaginary line drawn at 90° to the point of reflection.
- The angles of incidence and reflection are measured to the normal.
- The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence, the other side of the normal.
- On a graph, a line of best fit highlights the main pattern of the data, ignoring small errors.
Keywords
Protractor - a device used to measure angles
Normal - another way of saying ‘at 90°’ - a ‘normal line’ is at 90° to a surface
Reflect - to reflect off a surface means to hit the surface and ‘bounce’ off
Incident - an adjective meaning 'incoming'
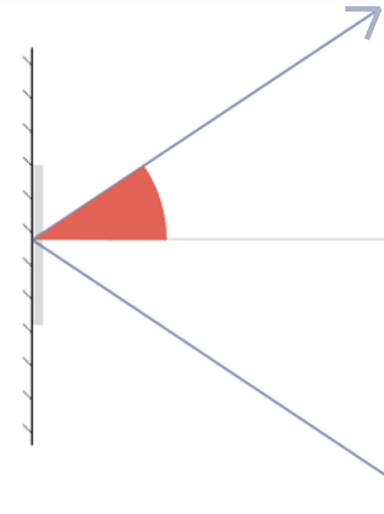
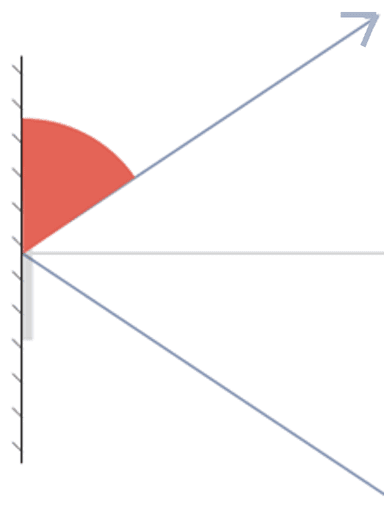
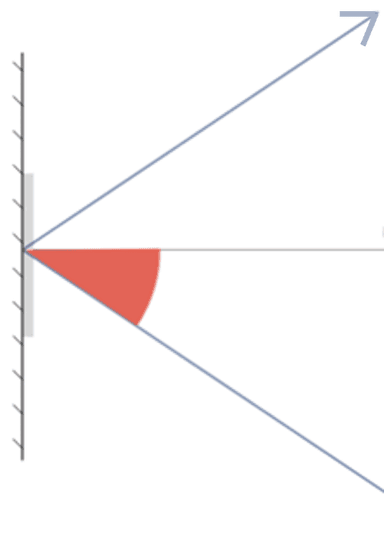
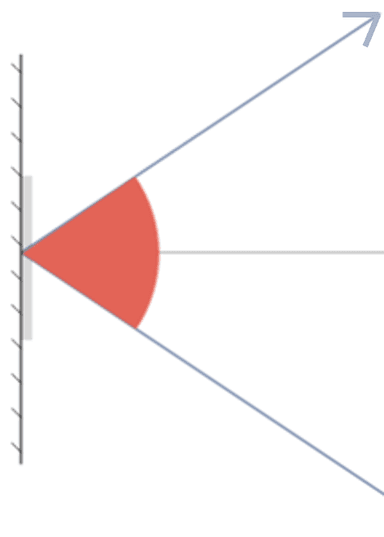
Angle of incidence - the angle between the incident ray and the normal when light hits a mirror
Common misconception
Some pupils think that a ray of light can reflect off at an angle different to that at which it hits a plane mirror and perhaps in several directions.
Give pupils practical experience of measuring the angles at which light reflects off a plane mirror to confirm the correct rules; share results to confirm; and discuss potential sources of error that may lead to small discrepancies.
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Reflecting light from mirrors, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Reflecting light from mirrors, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Sound, light and vision unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Class practical: ray boxes (and power supplies if needed), suitable mirrors, protractors. Please see the additional materials for teacher and technician notes on this practical.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
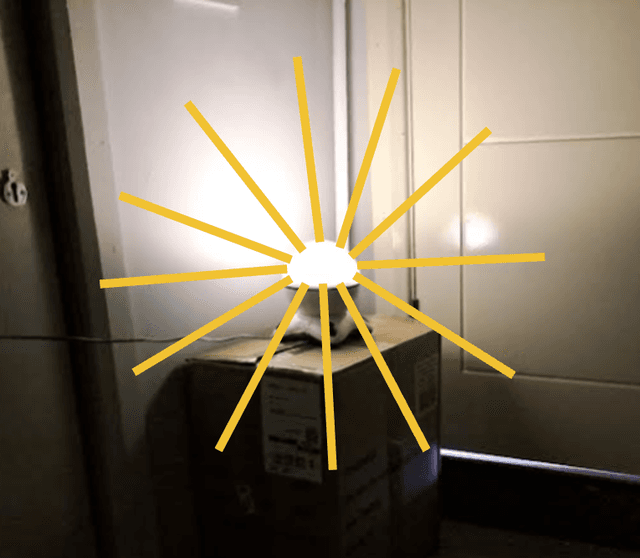
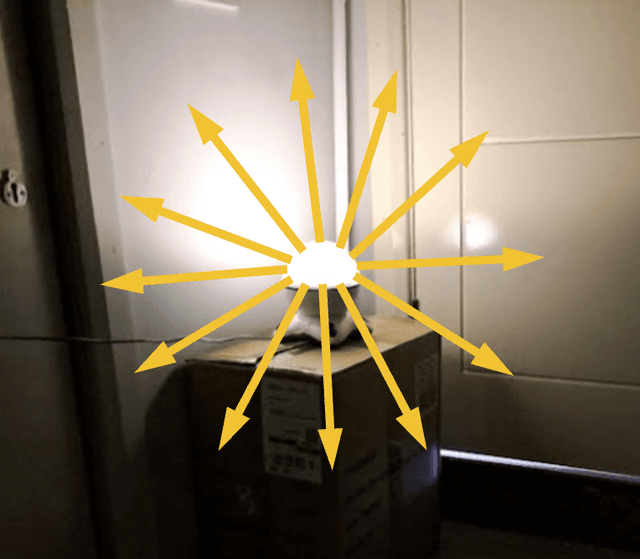
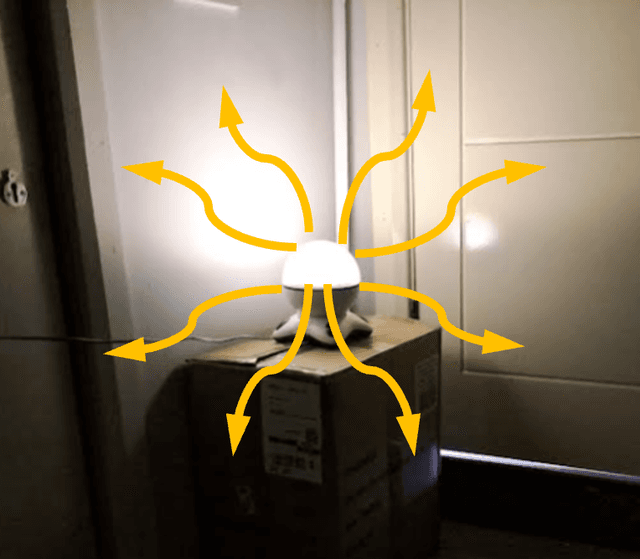
Q1.Which of the following images correctly shows light rays coming from a lamp?

Q2.Which of the following units are angles measured in?
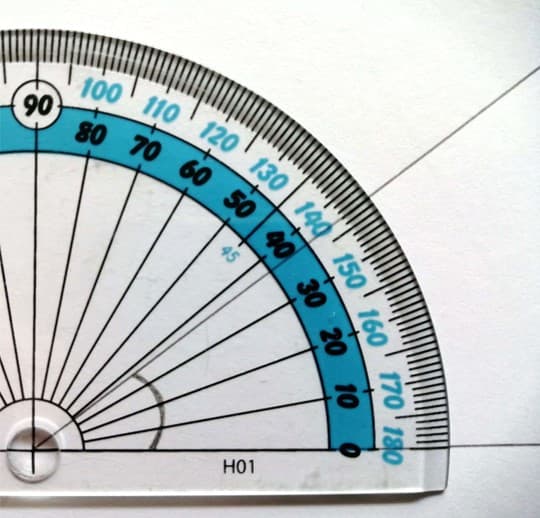
Q3.What is the size of the marked angle?

Q4.The size of a full turn is °.
Q5.Which of the following pieces of equipment is used to measure angles?
Q6.What is the size of the marked angle between the two lines in the image?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following key terms to their definitions.
An imaginary line drawn at 90° to the point of reflection at a mirror.
An arrow showing the direction of light before it hits a mirror.
An arrow showing the direction of light after it hits a mirror.
Q2.The diagrams show a light ray reflecting from a mirror. In which diagram is the angle of incidence marked?