Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Making a pure dry sample of a soluble salt
I can carry out a multistage chemical procedure to make a pure dry sample of a soluble salt.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Making a pure dry sample of a soluble salt
I can carry out a multistage chemical procedure to make a pure dry sample of a soluble salt.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Reacting a metal oxide with an appropriate acid can form a desired salt and water.
- Adding metal oxide to excess ensures that the acid fully reacts to form salt and water.
- Excess metal oxide can be removed by filtration so that the filtrate contains only salt and water.
- Water can be removed from the salt by evaporation.
Keywords
Soluble - When a substance dissolves in a liquid, it is described as soluble in that liquid.
Excess reactant - any reactant present in a greater amount than is necessary to completely react with the limiting reactant
Filtration - a technique to separate insoluble solids from a liquid by passing the mixture it is in through a filter
Crystallisation - a process that forms solid crystals from a saturated solution by evaporating the solvent
Common misconception
Pupils often do not understand that observing excess metal oxide in the reaction mixture means that the acid has fully reacted.
Emphasise how to observe the end of the reaction and what these observations mean, i.e. excess metal oxide in the reaction mixture or using pH paper to indicate the solution is neutral. Both are evidence of the acid having fully reacted.
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Making a pure dry sample of a soluble salt, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Making a pure dry sample of a soluble salt, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Making salts unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
dilute sulfuric acid, copper oxide, measuring cylinder, Bunsen burner, tripod and gauze, spatula, beakers, universal indicator paper, filter paper and funnel, conical flask and evaporating dish
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - chemicals
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.How can you increase the concentration of a solution?
Q2.What is the purpose of filtration?
Q3.Which of the following equations represent neutralisation reactions used for making salts?
Q4.Match each salt with the reactants that can be used to make it.
magnesium and hydrochloric acid
copper oxide and sulfuric acid
copper oxide and nitric acid
Q5.What is a saturated solution?
Q6.What happens during crystallisation?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Reactions between an acid and a metal, or between an acid and certain metal compounds (like hydroxide, oxide or carbonate), are all types of reactions.
Q2.An insoluble metal oxide reacts with an acid to make a soluble salt. What are the main steps, in any order, needed to make pure crystals of the soluble salt.
Q3.An insoluble metal oxide reacts with an acid to make a soluble salt. Put each step in the correct order to describe how a metal oxide is reacted with an acid, making sure all the acid has reacted.
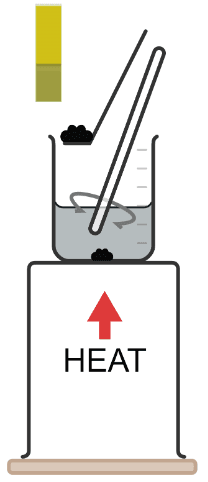
Q4.The undissolved impurity in a salt solution that remains in filter paper after filtration is called the .
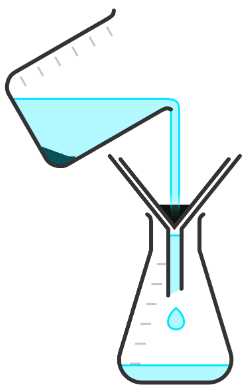
Q5.Put each step in the correct order to describe how to obtain crystals of salt from a pure salt solution.
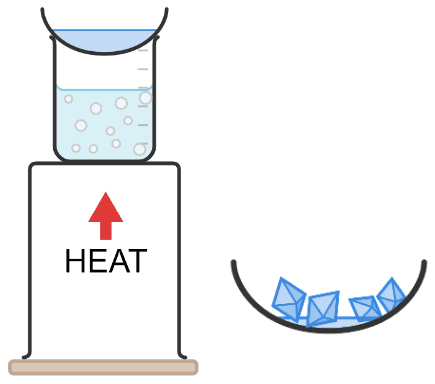
Q6.Match these key terms to the correct definitions.
the property of a substance that dissolves in a liquid
the reactant left over after a reaction is complete
a technique for separating insoluble solids from a liquid
forming solid crystals from a saturated solution by evaporation
the reactant that is fully used up during a reaction


