Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
Determining ionic formulae
I can deduce the formulae of ionic compounds (including oxides, hydroxides, halides, nitrates, carbonates and sulfates) given the formulae of the constituent ions.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
Determining ionic formulae
I can deduce the formulae of ionic compounds (including oxides, hydroxides, halides, nitrates, carbonates and sulfates) given the formulae of the constituent ions.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- An empirical formula is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
- The formula of an ionic compound is an empirical formula, as there is no definite quantity of each ion.
- Ionic compounds ending with "–ide" only contain a metal and a non–metal ion.
- Polyatomic ions are ions that are made up of more than one type of atom.
- Ionic compounds ending with "–ate" always contain at least three elements, one of which is oxygen.
Keywords
Empirical formula - The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Polyatomic ions - Ions that are made up of more than one type of atom.
"–ide" - The name ending for a compound with a metal and non–metal present, for example, potassium iodide (KI).
"–ate" - The name ending for a compound with three or more elements present (one of which is oxygen), for example, potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄).
Common misconception
Using ionic charges to determine the empirical formulae, especially with polyatomic ions. Standard notation is difficult and confusing, e.g. when to use superscripts, subscripts or brackets.
At this stage, pupils will need to just learn the the formulae of the polyatomic ions and accept that a full explanation will come later in their chemistry learning. Provide pupils with plenty of practice of writing and using ionic formulae.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Determining ionic formulae, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Determining ionic formulae, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Structure and bonding unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Ions form through the loss or gain of ...
Q2.When a nitrate ion forms, it gains one electron. What charge does a nitrate ion have?
Q3.True or false? Non–metal atoms gain electrons to become more stable, negatively charged ions.
Q4.Which of the following statements about ammonium nitrate, NH₄NO₃, are correct?
Q5.Match the following terms to the correct definitions.
The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
The regular arrangement of atoms or ions in a 3D space.
Atom or molecule with a charge due to the gain or loss of electrons.
Q6.Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound. Which of the following statements does not describe magnesium chloride?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following key terms to the correct definition.
Simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Shows the actual number of atoms of each element in a compound.
Ions made of more than one type of atom.
Name ending for a compound with a metal and singular non–metal.
Name ending for a compound with 3 or more elements, one being oxygen.
Q2.The molecular formula for hydrogen peroxide is H₂O₂. What is its empirical formula?
Q3.Which of the following are examples of ionic compounds with names ending with –ide?
Q4.Which of the following are examples of polyatomic ions?
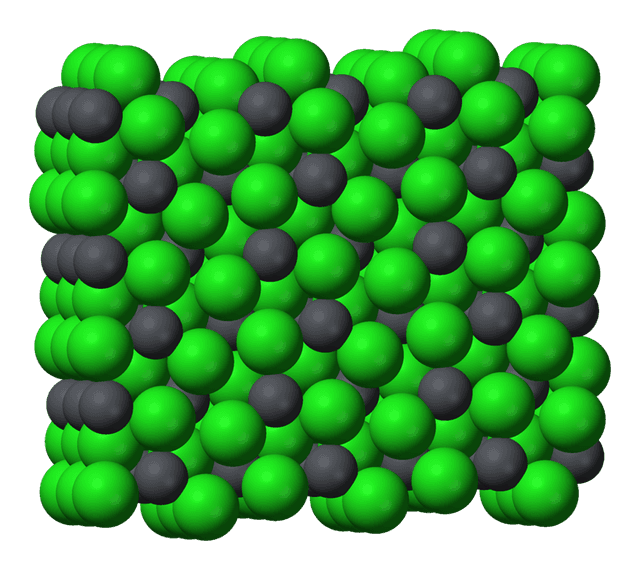
Q5.The image shows the ionic compound lead(II) chloride. What is the empirical formula for lead(II) chloride?