Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- OCR
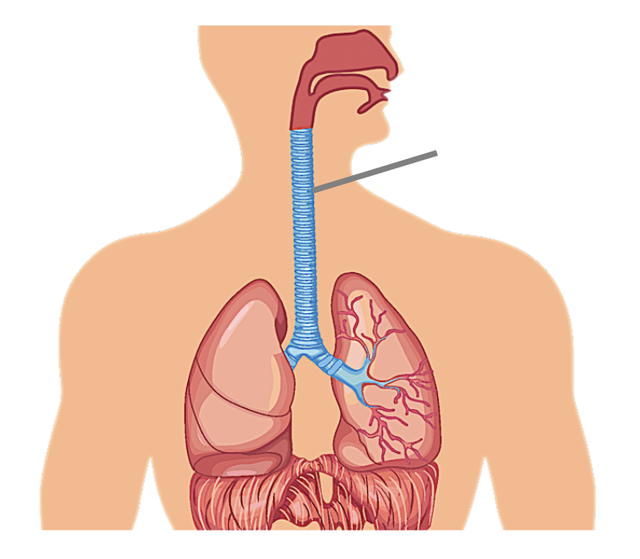
Air pathway from the atmosphere to alveoli and gaseous exchange
I can describe the pathway of air from the atmosphere through to gaseous exchange in my lungs.
- Year 10
- OCR
Air pathway from the atmosphere to alveoli and gaseous exchange
I can describe the pathway of air from the atmosphere through to gaseous exchange in my lungs.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Air enters through the mouth/nose, travels down the trachea and bronchi to the alveoli where gaseous exchange occurs.
- Gaseous exchange is the process of diffusion where oxygen moves into the body and carbon dioxide moves out.
- Diffusion is the movement of particles (e.g. oxygen) from an area of high to an area of low concentration.
- Gaseous exchange increases during/immediately after exercise.
Keywords
Trachea - the windpipe that connects the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi, allowing air to pass to and from the lungs
Bronchi - two main branches off the trachea that lead to the lungs, where they further divide into bronchioles
Alveoli - tiny air sacs in the lungs where gaseous exchange between air and blood takes place
Gaseous exchange - the process where oxygen and carbon dioxide are switched between the lungs or the muscles and the bloodstream
Diffusion - the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Common misconception
Gaseous exchange only involves oxygen.
Gaseous exchange is when oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the lungs and the blood, and then between the blood and muscle tissues.
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Air pathway from the atmosphere to alveoli and gaseous exchange, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Air pathway from the atmosphere to alveoli and gaseous exchange, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physical education lessons from the Anatomy and physiology: the cardio-respiratory system unit, dive into the full secondary physical education curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The cardiovascular system links with the system to get air in to the body to the working muscles.
Q2.Where does air enter our body?
Q3.Exercise increases heart rate as more oxygen is required around the body.
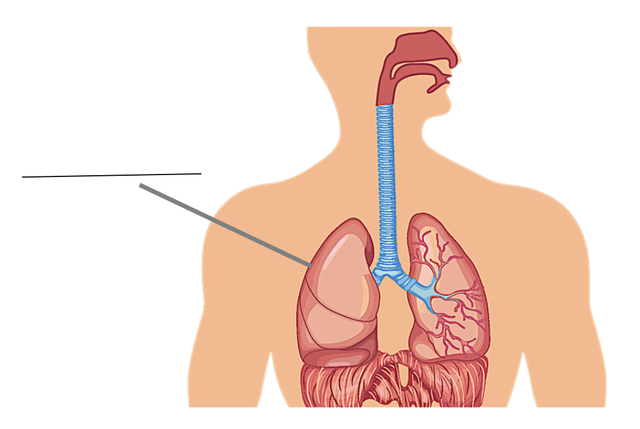
Q4.Name the organ that has been identified in the image below.
Q5.Match the correct component to the body system it is part of.
respiratory system
muscular system
cardiovascular system
skeletal system
Q6.The process where oxygen and carbon dioxide are switched between the lungs or the muscles and the bloodstream is known as?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which part of the respiratory system is identified in the image below?