Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- OCR
Double circulatory system and structure of the heart
I can describe the pathway of blood through the double circulatory system and explain its importance in maintaining efficient blood flow.
- Year 10
- OCR
Double circulatory system and structure of the heart
I can describe the pathway of blood through the double circulatory system and explain its importance in maintaining efficient blood flow.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Deoxygenated blood travels from the body into the heart's right side then through the pulmonary artery to the lungs.
- The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart then out the aorta to the body.
- Valves in the heart prevent the backflow of blood.
- The heart is a double circulatory pump. The pulmonary circuit carries blood to the lungs then back to the heart.
- The systemic circuit carries oxygenated blood out of the heart to the body tissues and returns with deoxygenated blood.
Keywords
Atria - the upper chambers of the heart. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood and the left receives oxygenated blood
Ventricles - the lower chambers of the heart that receive blood from the atria before pumping it out to the body/lungs
Valves - structural feature that prevents backflow of blood
Pulmonary circulation - carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lung then back to the left side of the heart
Systemic circulation - carries oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to the rest of the body. After delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body, the blood returns to the right side of the heart deoxygenated
Common misconception
Which side of the heart is the left when you look at the body and which side is oxygenated versus deoxygenated.
The left side of the heart is nearest your left armpit and carries oxygenated blood, the right side of the heart has deoxygenated blood (remember: LORD - left, oxygenated and right, deogygenated).
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Double circulatory system and structure of the heart, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 physical education lesson on: Double circulatory system and structure of the heart, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 physical education lessons from the Anatomy and physiology: the cardio-respiratory system unit, dive into the full secondary physical education curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Red and blue pens for oxygenated and deoxygenated blood diagrams.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following does the word cardiac relate to?
Q2.What is the substance carried to our working muscles within the blood that provides energy for exercise?
Q3. are a type of blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart at high pressure.
Q4.When you start exercising, your heart rate ...
Q5.The wall that divides the left and right sides of the heart is called the ...
Q6.Match the following body system with its main function.
allows movement when muscles contract to leverage bones
pumps blood to deliver oxygen/nutrients and remove waste products
enables gaseous exchange to get oxygen into the body
the heart, blood vessels and lungs that deliver oxygen to muscles
converts food we eat into nutrients we can use for energy, growth etc.
sends messages between the brain and different body parts
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The systemic circuit supplies oxygen to which two of the following areas?
Q2.The circuit transports blood to the lungs to collect oxygen and takes it back to the heart.
Q3.Which of the following refers to the two chambers at the top of the heart?
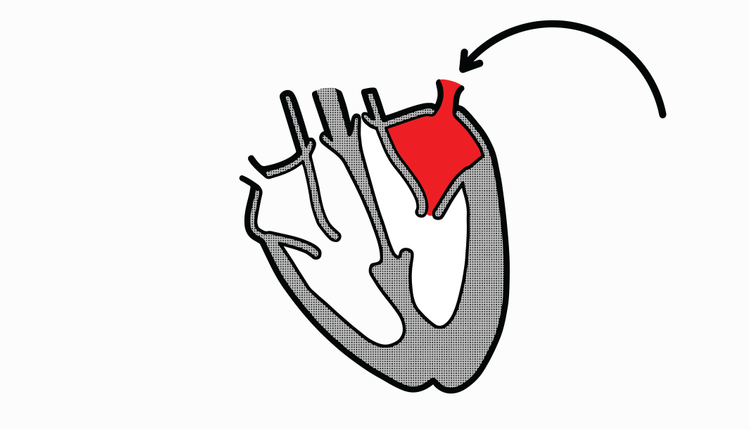
Q4.Name the chamber identified in red in the image below.
Q5.Match the following components of the circulatory system.
carries blood from the heart to the lungs
situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle
the biggest chamber of the heart before blood is pumped to the body
the biggest artery in the body carrying blood into systemic circuit
the main vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the right atrium
prevent backflow into heart after being pumped out of ventricles


